Manipulating a Word doc from within your application
- Load your application
- Add the Office Inside global extension template
- Right-click on the procedure that you will use to control word (this
needs to at least be a window in order to include an event handler) and choose Extensions
- Click Insert. Choose Add_MSWord_Object and click Select.
- You now have the ability to edit a word document from within that
procedure. From here, the best is to use the offdemo application
(particularly the Word_Main procedure) which will give you an idea of (a)
what you can do and (b) how to do it. Consult the
class section of this document which will show you how to use the
various methods and properties of the oiWord class.
Adding Spell Checking to your application
- Load your application
- Choose Template Utility from the IDE's
Application menu
- Choose ShowSpellingSuggestionsABC (found
under Class OfficeInside), and click the Select button.
You should now see a new procedure in your
application called oiShowSpellingSuggestions. This window is called by
Office Inside when it checks your spelling from within other procedures
in your application.
- Select the procedure(s) in your application that you
want to add Spell Checking support to
- Right-click on the procedure and choose Extensions
- If you already have an Add an MS Word object to
this procedure extension template listed for this procedure, skip to point
8, otherwise:
- Click Insert. Choose Add_MSWord_Object and click Select.
- Select the Add an MS Word object to this
procedure extension, and then click the Insert button
- Choose Word_SpellChecking and click the
Select button. At this point, there are a number of
template options you can change, namely - overriding the default alert
key, Include specific controls (or exclude specific controls) using the
template prompts.
- Click OK and compile your application!
Important Information!!!!
A Checkbox has been added to the Global Extension that should be checked in
order to use spell checking on a Clarion 6 RTF control. See the
section
below on C6 RTF controls for
instructions on changing the required RTF class property.
If you're not sure how to add an RTF control to your
window, take a look at the
FAQ section below.
Exporting a report to Word
If you have not done so already, add the OfficeInside
global extension to your application
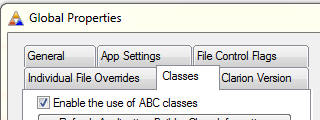
If this is a Legacy application, then you must check the
"Enable the use of ABC classes" checkbox in the Global Properties of your
Application on the Classes tab.
 In the extension templates of the Report procedure that
you want to export to Excel, add the "Add_MSWord_Object" template to the
templates there. In the template prompts, select "Reports" from the
Template Type.
In the extension templates of the Report procedure that
you want to export to Excel, add the "Add_MSWord_Object" template to the
templates there. In the template prompts, select "Reports" from the
Template Type.

If you have a FileExplorer extension added to this procedure, then check the
"Activate compatibility with file Explorer" checkbox, and ensure the "Base
Class" is set to "oiWord".
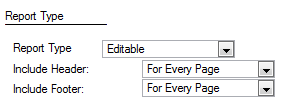
On the Report Type tab, there are a number of options you can set:
 Report Type should be set to Editable
You can select to include the Header and Footer on Every Page, Once (at the top
for the header or bottom for the footer), or never.
Report Type should be set to Editable
You can select to include the Header and Footer on Every Page, Once (at the top
for the header or bottom for the footer), or never.
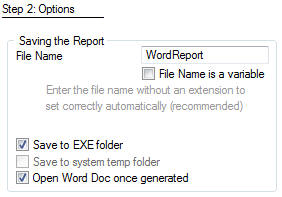
On the Options tab, you can set:
 The output file name (you can make this a
variable by checking the "file name is a variable" checkbox and entering a
variable name. You should not include the doc or docx extension though, as OfficeInside will populate
this correctly depending on which version of Excel is installed on your
user's PC.Save to EXE folder is self explanatory as is open Word Doc
once generated.
The output file name (you can make this a
variable by checking the "file name is a variable" checkbox and entering a
variable name. You should not include the doc or docx extension though, as OfficeInside will populate
this correctly depending on which version of Excel is installed on your
user's PC.Save to EXE folder is self explanatory as is open Word Doc
once generated.
Select the report’s Procedure from the Procedure Tree.
Press the Properties Button. Press the Actions Button. Press the Report
Properties Button. On the Report Target Tab, select for Report Target, “Ask at
Runtime.”
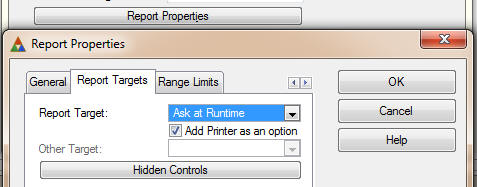
or if you prefer, you can stipulate to use Word as the other target.
Using Mail Merge
In this context the term mail merge is a word doc with a number of "Field"s in it that are replaced with values
from the data base and either printed, emailed or saved as multiple documents
when the Merge is "Finished". Typically your Word Doc would look something like:
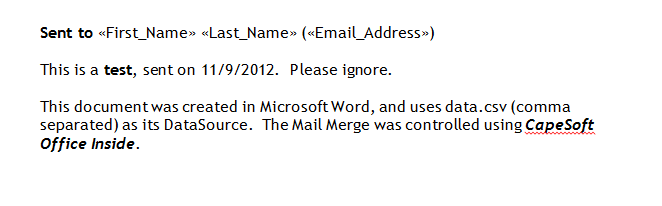
You can also
Create the Mail Merge Document at
runtime
You will notice in the document that there are 3 fields used: <<First_Name>>,
<<Last_Name>> and <<Email_Address>>. These 3 fields exist in your datasource.
Your datasource would typically be a csv file that would contain at least these
3 fields:
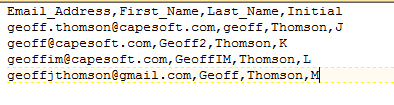
The first line of your CSV file must contain the field names that will be
used in the Word Doc to identify the fields in your data source. If you have a
new Word doc and you have not yet registered your datasource, then you need to
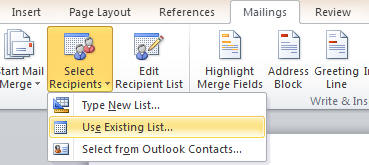
use the
Mailings tab and
Select Recipients
button to select the data source file from which to glean the data from (you can
use the
MailMergeSetDataSource method to get
OfficeInside to do this from within your application).
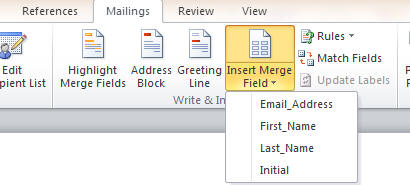
To use the fields from your datasource in the Word Doc, you need to use the
Mailings tab and
Insert Merge Field
button,
and all the fields of your datasource will be listed.
If you need to add more
fields to the datasource file, you need to first close MS Word, before editing your datasource file. The next time that you open your Word Doc for editing, your new
field(s) will be available for use in the master document.
NOTE: Spaces in your datasource's field name get changed to _ character in the
Merge Field name
To control your Mail Merge doc from your Clarion application here's what you
need to do:
- If you have not done so already, add the OfficeInside
global extension to your application.
- In the extension templates of procedure from where you'll be
controlling the sending of the mail merged document, add the "Add_MSWord_Object" template to the
templates there. In the template prompts, select "Mail Merge" from the
Template Type.
On the Init tab, decide if you want to display the Word doc or not (check
"Make Word Visible" if you do), and leave the other options to their
defaults.
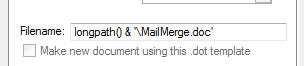
On the Open tab, set the Filename to the name of the Word Doc that you want
to use for the mail merge (note: it must contain the fully qualified path):
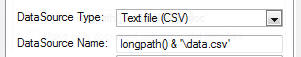
On the Data tab, choose a DataSource Type, and the name of the DataSource
(if you are using a variable, then you must make sure that your variable is
set to point to the correct datasource file before the template embed code
uses it) (note: it must contain the fully qualified path):
 This could also be an xls file (for type
csv).
This could also be an xls file (for type
csv).
On the Settings tab, choose the Merge type (Email/Printer/New Document) from
the "Merge To" drop down.
If you select Email, then you need to set the "Email Address field name"
(the field name in the data source used for the email address) and the
"Email Subject".
On the Merge tab, you can select the event that triggers the Mail Merge (you
can use a control in your procedure, as the window opens, or a handcoded
event).
On the Close tab, select the trigger to close the Mail Merge document.
NOTE: If you have a dotx file (template file) that you want to use for the
mailmerge (to add the mailmerge at runtime), then you must close the dotx
and save the new mailmerge doc as a docx in order to ensure that the dotx
file does not remain attached to the csv file for the mailmerge addresses.
Creating the Mail Merge Document at runtime
Converting a Word Macro into
your application
Microsoft have developed a scripting language that allows you to
automatically perform a sequence of tasks in Word. The sequence of commands is
called a macro. Unfortunately (as of writing this doc using Word 2010), you are
not able to use the right-click menu during Macro Recordings, which inhibits you
from generating a lot of macro functionality. However, you are still able to do
a number of tasks using the menu items. First thing is to record a macro in Word and
then we'll work through converting the generated VB script code in the following manner:
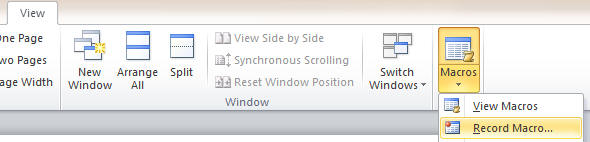
In your word doc, from the View menu, select the Record Macro in the Macros
drop down:
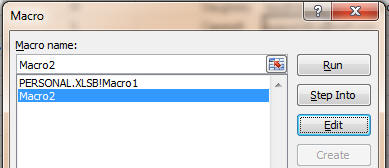
The Record Macro item now changes to a Stop Recording item. When you have
finished the sequence of instructions that you're wanting to perform, click the
Stop Recording item, and then use the View Macros to show the macro that you've
just recorded. Highlight the macro you just recorded, and click the Edit button
Now follow the steps in
Converting macro code to Clarion code
to convert your macro code to Clarion code.
This section describes the various classes which make up "Office Inside".
Each class contains methods and properties, which are documented below.
Each method is documented by giving the method name, the parameters, an example
of how to code the method, a list describing what the method does, and additional
comments below.
The oiWord Class - Introduction
The oiWord class is a "wrapper" class, which is used by the templates
and by other classes as the "communication" layer between Office Inside
and MS Word. Should you wish to write code which communicates "directly"
with MS Word, this is the class you're looking for.
oiWord Class Methods
See
Properties as well.
AlignCenter
AlignCenter( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Centers the currently selected text on the page
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced
Example
| Example |
MyWord.AlignCenter ()
TempByte = MyWord.AlignCenter () |
AlignJustify
AlignJustify ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Justifies the currently selected text
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced
Example
| Example |
MyWord.AlignJustify ()
TempByte = MyWord.AlignJustify () |
AlignLeft
AlignLeft ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Aligns the currently selected text to the left.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced
Example
| Example |
MyWord.AlignLeft ()
TempByte = MyWord.AlignLeft () |
AlignRight
AlignRight ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Aligns the currently selected text to the right.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced
Example
| Example |
MyWord.AlignRight ()
TempByte = MyWord.AlignRight () |
Bold
Bold ( byte pOption=oiw:BoldToggle ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Makes text bold / not bold
- pOption can be one of the following equates:
- oiw:BoldOn
- oiw:BoldOff
- oiw:BoldToggle
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced
Example
| Example |
MyWord.Bold (oiw:BoldOn)
TempByte = MyWord.Bold (oiw:BoldOn) |
CentimetersToPoints
CentimetersToPoints ( string pCentimeters ) ,string
Description
- Converts from centimetres to
points. 1 cm = 28.35 points. The pCentimetres
parameter and the return parameter are both strings however, as we
figured this would make your life easier to code (see examples
above).
- See also InchesToPoints,
LinesToPoints,
MillimetersToPoints,
PicasToPoints,
PixelsToPoints,
PointsToCentimeters,
PointsToInches,
PointsToLines,
PointsToMillimeters,
PointsToPicas, and
PointsToPixels.
Example
| Example |
loc:Points = MyWord.CentimetersToPoints(1.5)
MyWord.Update(oiw:PageLeftMargin, MyWord.CentimetersToPoints(1.5))
|
CheckGrammar
CheckGrammar ( *string pText ) ,byte
Description
- Checks the grammar in the text passed as pText.
- Returns true (1) if there were no grammar errors, false (0) if there
were errors, and a value greater than 1 if an internal error occurred.
- ( Current limitation of 1000 characters )
Example
| Example |
| TempByte = MyWord.CheckGrammar (StringVar) |
CheckSpelling
CheckSpelling
( string pText, byte pSilent ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Checks the spelling in the text passed as pText.
- Returns true (1) if there were no spelling errors, false (0) if
there were errors, and a value greater than 1 if an internal error
occurred.
- When you call this method, the queue (property) called self.WordsQ
is populated with any spelling suggestions.
- ( Current limitation of 1000 characters )
- ( This documentation must be redone )
Example
| Example |
StringVar = 'This is spelld wrongg'
TempByte = MyWord.CheckSpelling (StringVar)
if MyWord.CheckSpelling (loc:Var1, false, false) = true
loc:Var1 = MyWord1.TempCString
... |
CheckSpelling_AddToIgnoredWords
CheckSpelling_AddToIgnoredWords ( string pText ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Used by the templates when spell checking. Adds the word
passed as pText to a list of words to be ignored when spell
checking.
Example
| Example |
| MyWord.CheckSpelling_AddToIgnoredWords ('CapeSoft') |
CheckSpelling_IsWordIgnored
CheckSpelling_IsWordIgnored ( string pText ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Used by the templates when spell checking
- Returns true (1) if the word pass as pText is in the list
of words to be ignored
Example
| Example |
if MyWord.CheckSpelling_IsWordIgnored ('CapeSoft')
= true
...
|
CloseDoc
CloseDoc ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Closes the currently open document
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced
Example
| Example |
MyWord.CloseDoc()
TempByte = MyWord.CloseDoc() |
CloseFooter
CloseFooter ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Used after you have called the OpenFooter method to make the
footer section of the document "inactive", so that you can continue
working on the document.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced
Example
| Example |
| MyWord.CloseFooter() |
CloseHeader
CloseHeader ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Used after you have called the OpenHeader method to make the
header section of the document "inactive", so that you can continue
working on the document.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced
Example
| Example |
| MyWord.CloseHeader() |
Copy
Copy ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Copies the current selection to the clipboard
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced
Example
| Example |
MyWord.Copy()
TempByte = MyWord.Copy() |
CountCharacters
CountCharacters ( ) ,long
Description
- Returns the number of characters in the document, or a negative
value if an error occurred.
Example
| Example |
| TempLong = MyWord.CountCharacters () |
CountOpenDocs
CountOpenDocs ( ) ,long
Description
- Returns the number of currently open documents
- Returns a value less than 0 if an error occurred
Example
| Example |
| TempLong = MyWord.CountOpenDocs() |
CountTables
CountTables ( ) ,long
Description
- Returns the number of tables in the current document, or a negative
value if an error occurred.
Example
| Example |
| TempLong = MyWord.CountTables () |
DocumentStatistics
DocumentStatistics
(long statistic), long
Description
Loads the entire contents of a file into a string. If the string passed is not
large enough the required size is returned.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| long statistic |
Indicates the statistic to be retrieved. Must be one of the following values:
- oiw:StatisticCharacters: Count of characters.
- oiw:StatisticCharactersWithSpaces: Count of characters including spaces.
- oiw:StatisticFarEastCharacters: Count of characters for Asian languages.
- oiw:StatisticLines: Count of lines.
- oiw:StatisticPages: Count of pages.
- oiw:StatisticParagraphs: Count of paragraphs.
- oiw:StatisticWords: Count of words.
|
Return Values
The method returns -1 for failure, or the requested statistic if it succeeds.
Example
| Example |
numWords long
pExcel class(oiExcel)
end
code
numWords = pExcel.DocumentStatistics(iw:StatisticWords)
if numWords < 0
Message('Could not fetch the word count.')
else
Message('The document contains ' & numWords & ' words.')
end |
See Also
StringToFile - write the content of a string to a file on disk.
Cut
Cut ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Cuts the current selection to the clipboard
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced
Example
| Example |
MyWord.Cut()
TempByte = MyWord.Cut() |
FindText
FindText (string pText), long
Description
Searches the document for the passed strings and returns 1 and selects the string if
found, or returns zero and does not change current selection if the string does not exist in the document.
This can be called multiple times to find each instance of the string in the
document (for example to make each instance of the string bold - see the
example below).
Note: Each subsequent call will find and highlight the next text
in the document, so it's important to note that the exact same FindText call
might return 0 if there are no subsequent strings of that nature in the
document.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| string pText |
The string to search for in the document |
Return Values
Returns 1 if successful and selects the string that was found,
or if the string cannot be found it returns zero.
Examples
| Example |
loop while myWord.FindText('Hello
')
myWord.Bold(oiw:BoldOn)
end |
GetFileName
GetFileName (), string
Description
Returns the full path and name of the
current file. If the document has not been save, it will return the name of the
document, such as 'Document1'.
Parameters
None
Return Values
Returns the full path and name of the current document on
disk, for example 'C:\Documents\Personal\Accounts.doc'. If there is an error, or
not document has been opened then a blank string is returned. If the current
document has not been saved (and hence does not exist on disk) then the current
name of the document is returned, for example: 'Document1'
Examples
| Example |
| Message('Current document file name
is: ' & myWord.GetFileName)
|
ErrorTrap
ErrorTrap( string pErrorString, string pFunctionName )
Description
- This method is called when an error occurs. Office Inside
provides embed points for this method (before parent call, and after
parent call) where you can put code to deal with any errors Office
Inside experiences (see the example code above - note the grey text
indicates code generated by the Office Inside template, the black
text is what you would add).
- By default any errors that Office Inside encounters will be
dealt with as follows:
- First, this ErrorTrap method is called, where you can act on the
error message as shown in the example code above.
- Second, Outlook might display a message of its own. You
can suppress all messages by ticking the Suppress Error Messages
check box in the procedure extension template.
- Note 1 : Even if you suppress error messages the ErrorTrap
method will still be called.
- Note 2 : The Suppress Error Messages checkbox simply
generates a line of code that sets the SuppressErrorMessages
property to true. You can set this property manually if you
prefer.
Example
| Example |
MyWord1.ErrorTrap
PROCEDURE (string
pErrorString, string
pFunctionName)
code
parent.ErrorTrap(pErrorString, pFunctionName)
if
pErrorString = 'Init
Failed'
Message('Could
not initialise Word! Please ensure that MS Word is installed.')
end |
GetFontColor
GetFontColor ( ) ,long
Description
- Returns the color (value) of the currently selected text.
- If the color value (long) matches any of the standard Clarion color
equates, the method will return that equate (e.g. COLOR:Green), or
it will simply return a long (color).
Example
| Example |
| TempLong = MyWord.GetFontColor() |
GetFontName
GetFontName ( ) ,string
Description
- Returns the font name (font) for the currently selected text.
Example
| Example |
| TempString = MyWord.GetFontName() |
GetFontNames
GetFontNames ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Returns true (1) if no problems were encountered.
- Populates a queue (property) called self.FontNamesQ with a list
of all available fonts.
Example
| Example |
| MyWord.GetFontNames () |
GetFontSize
GetFontSize ( ) ,long
Description
- Returns the current font size
- Returns a negative value if an error occurred
Example
| Example |
| TempLong = MyWord.GetFontSize() |
GetInfo
GetInfo ( byte pOption ) ,string,proc
Description
- This is a wrapper method which can be used to get various information,
and read various properties, depending on the parameters which you
pass.
- The pOption parameter can be one of the GetInfo/Update
Equates.
- The string which is returned contains the information pertaining
to the parameter you requested information about.
Example
| Example |
| TempString = MyWord.GetInfo (oiw:GetUserName) |
GetNameOfDictionary
GetNameOfDictionary ( ) ,string
Description
- Returns the name (and full path) of the dictionary currently being
used (to check spelling)
Example
| Example |
| TempString = MyWord.GetNameOfDictionary() |
GetObjects
GetObjects( ) ,long
Description
- Sets the main oiObject handles that you'll need to interact with the
Word COM objects. These are: ActiveDocument, ActiveWindow, Selection,
Tables, Paragraphs
- Returns a 0 if an error occurred.
Example
| Example |
| TempLong = MyWord.GetObjects() |
GetSelectionEnd
GetSelectionEnd ( ) ,long
Description
- Returns the position of the last selected character within the document.
- Returns a negative value if an error occurred.
Example
| Example |
| TempLong = MyWord.GetSelectionEnd() |
GetSelectionStart
GetSelectionStart ( ) ,long
Description
- Returns the position of the first selected character within the
document.
- Returns a negative value if an error occurred.
Example
| Example |
| TempLong = MyWord.GetSelectionStart() |
GetText
GetText ( byte pScope=oiw:GetText_All ) ,byte,proc
Description
- This method updates an Office Inside property called
self.TempCString (*cstring) with the text found in the currently
loaded document. Use the pScope parameter to tell this method
which text you want, passing one of the following values / equates:
- oiw:GetText_CurrentSelection - returns currently
selected text
- oiw:GetText_All - returns all text in document
- This method returns a byte indicating whether the method worked
successfully (in which case "1" is returned), or whether
an error occurred (in which case "0" is returned).
- NOTE: The self.TempCString property
should be treated as read-only...
Example
| Example |
if MyWord1.GetText (oiw:GetText_CurrentSelection) = true
stop(MyWord1.TempCString)
end |
GotoEndOfDoc
GotoEndOfDoc ( ), byte, proc
Description
Moves the cursor to the end of the current document.
Return Values
Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Examples
| Example |
MyWord.GotoEndOfDoc()
if not MyWord.GotoEndOfDoc()
Message('Could not go to the
end of the document, an error occured.')
end |
GotoItem
GotoItem(long pItem, <long pDirection>,
<long pName>, <long pCount>),
long, proc
Description
Moves the cursor to a location within the document, based on the
parameters which you pass. Can be used to navigate to a position in
the document based on a line, paragraph, bookmark, character position
etc. The
pItem parameter is used to specify which item
to go to, and the
pDirection parameter specifies which
one of those items to go to (the first, last etc.). You can set the
pDirection to
oiw:GotoAbsolute
and then use the
pCount parameter to specify the number
of the item to go to (for example the 4th line in a document).
Note: If the pItem
parameter is
oiw:GoToBookmark,
oiw:GoToComment,
oiw:GoToField, or
oiw:GoToObject,
this parameter specifies a name and the pName field must be passed to
specify which item is referred to.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| long pItem | The item to go to. Can be one of the GoTo equates:
- oiw:GoToBookmark - goes to the
bookmark specified by the pName.
- oiw:GoToSection - goes to the
section specified by the pDirection and
pCount parameters.
- oiw:GoToPage - goes to the page
specified by the pDirection and
pCount parameters.
- oiw:GoToTable - goes to the table
specified by the pDirection and
pCount parameters.
- oiw:GoToLine - goes to the line
specified by the pDirection and
pCount parameters.
- oiw:GoToFootnote - goes to the
footnote specified by the pDirection and
pCount parameters.
- oiw:GoToEndnote- goes to the endnote
specified by the pDirection and
pCount parameters.
- oiw:GoToComment - goes to the
comment specified by the pName.
- oiw:GoToField - goes to the field
specified by the pName parameter.
- oiw:GoToGraphic - goes to the
comment specified by the pDirection and
pCount parameters.
- oiw:GoToObject - goes to the
comment specified by the pName parameters.
- oiw:GoToEquation - goes to the
comment specified by the pDirection and
pCount parameters.
- oiw:GoToHeading - goes to the
comment specified by the pDirection and
pCount parameters.
- oiw:GoToSpellingError - goes
to the comment specified by the pDirection and
pCount parameters.
- oiw:GoToGrammaticalError -
goes to the comment specified by the pDirection and
pCount parameters.
- oiw:GoToPercent - goes to the
comment specified by the pDirection and
pCount parameters.
- oiw:GoToProofreadingError - goes to
the comment specified by the pDirection and
pCount parameters.
|
| long pDirection |
Specifies which items to go to, can
be used in combination with the pCount parameter. For example if
pDirection is set to oiw:GoToPrevious, then the count parameter can
specify how many previous to go to (setting it to 4 will go to 4 items
previous to the current one). May be one of the following values:
- oiw:GoToAbsolute - goes to a specific item, for example the 2nd
table or 12th line in a document. Use the pCount parameter to
specify which instance of the item to go to.
- oiw:GoToFirst - goes to the first occurrence of the item
specified by the pItem parameter (table, line, paragraph etc.)
- oiw:GoToLast - goes to the last occurrence of the item specified
by the pItem parameter (table, line, paragraph etc.)
- oiw:GoToNext - goes to the next occurrence of the item specified
by the pItem parameter (table, line, paragraph etc.). Can be use in
conjunction with the pCount parameter to move that number of the
specified items.
- oiw:GoToPrevious - goes to the previous occurrence of the item
specified by the pItem parameter (table, line, paragraph etc.). Can
be use in conjunction with the pCount parameter to move that number
of the specified items.
- oiw:GoToRelative - moves the number of
pItems indicated by the
pCount parameter relative to the current item. For example can be
used to go four lines down from the current one.
|
Returns Values
Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced and
false (0) if an error occurs. In the case of an error the ErrorTrap
method will be called with a string indicating what error occurred.
Examples
| Example |
MyWord.GotoItem(oiw:GoToLine, oiw:GoToLast)
MyWord1.GotoItem(oiw:GoToBookmark, , 'FirstName')
MyWord1.GotoItem(oiw:GoToFootnote, oiw:GotoFirst)
MyWord1.GotoItem(oiw:GoToLine, oiw:GotoRelative, , 4)
MyWord1.GotoItem(oiw:GoToPage, oiw:GotoPrevious, , 2)
MyWord1.GotoItem(oiw:GoToEndNote, oiw:GoToAbsolute, , 5)
MyWord1.GotoItem(oiw:GoToTable, oiw:GotoNext)
MyWord1.GotoItem(oiw:GoToField, , 'Date')
|
HideToolbar
HideToolbar ( long pToolbar ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets a MS Word toolbar to be hidden. For a list of valid
equates which can be used, click here.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.HideToolbar (oiw:ToolbarStandard)
TempByte = MyWord.HideToolbar (oiw:ToolbarStandard)
|
InchesToPoints
InchesToPoints ( string pInches ) ,string
Description
- Converts from inches to points. 1 inch = 72 points. The pInches parameter and the return
parameter are both strings however, as we figured this would make
your life easier to code (see examples above).
- See also CentimetersToPoints,
LinesToPoints,
MillimetersToPoints,
PicasToPoints,
PixelsToPoints,
PointsToCentimeters,
PointsToInches,
PointsToLines,
PointsToMillimeters,
PointsToPicas, and
PointsToPixels.
Example
| Example |
loc:Points = MyWord.InchesToPoints(1.6875)
MyWord.Update(oiw:PageLeftMargin, MyWord.InchesToPoints(1.6875))
|
Init
Init ( byte StartVisible=1, byte EnableEvents=1 ) ,byte,proc
Description
- This method does several things, which can be summed us as "Getting
everything ready so you can call the other methods in this class".
This involves... (
To do )
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
- Note: The first time you initialize an oiWord object (after
starting your app), it might take a second or two to start an instance
(process) of MS Word, which it then uses. Any subsequent objects
that you initialize will first check to see whether they can use that
existing instance of MS Word before they start their own instance.
This speeds up the method significantly, especially for doing things
like using the Spell Checker. This is all taken care of for
you by the dll, and is mentioned here purely for those who are interested.
When your app closes, any instances (processes) of MS Word that the
dll started will be closed for you automatically.
( Must redo this... )
- Note: You can also set whether Word is visible after you have
called the Init method by using the Update method, passing
oiw:ApplicationVisible.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.Init()
TempByte = MyWord.Init() |
InsertBreak
InsertBreak ( long pBreakType=oiw:PageBreak ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Inserts a break into the current document. See the
Break-Types Equates which you can pass
as the
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.InsertBreak ()
MyWord.InsertBreak (oiw:PageBreak)
MyWord.InsertBreak (oiw:TextWrappingBreak) |
InsertPicture
InsertPicture ( string FileName ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Inserts a picture (image) into the current document, at the current
selection.
- Before calling this method, you can set the ImageProperties
property to control how the image will be inserted. For
example:
MyWord.ImageProperties.ScaleWidth =
80 ! 80 percent of original width
MyWord.ImageProperties.ScaleHeight = 80 ! 80 percent of
original height
MyWord.InsertPicture ('c:\mypic.bmp')
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.InsertPicture ('c:\mypic.bmp')
TempByte = MyWord.InsertPicture ('c:\mypic.bmp') |
InsertTable
InsertTable ( long NumColumns, long NumRows ) ,long,proc
Description
- Inserts a table into the current document, at the current selection
/ position.
- Returns 0 if a problem occurred, or the number of tables ( the table
you just inserted will be the last table in the document / i.e. the
highest number / i.e. the table number that is returned ) if the table
was inserted successfully.
- TIP : If you have for
example three tables in a document, and add a fourth table, this method
would return the value "4". If you then deleted a
table (say the second table that you inserted), then insert another
table, this method would again return "4". What was
table 3 before you deleted table 2 would now become table 2, the "old"
table 4 would become table 3, and the new table will be table 4.
In other words, tables don't keep their table numbers if you start
deleting tables.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.InsertTable (6, 3)
TempByte = MyWord.InsertTable (6, 3) |
InsertText
InsertText ( string pText, byte pOption=0 ) ,byte,proc or
( *cstring pText, byte pOption=0 ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Inserts text into the current document.
- pOption can be one of the following values:
- 0 - default value. text is inserted at or over the
current selection
- 1 - text is inserted before the current selection
- 2 - text is inserted after the current selection
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.InsertText ('Hello World')
TempByte = MyWord.InsertText ('Hello World') |
InsertTextbox
InsertTextbox ( string pText ) ,byte,proc
Description
Inserts a textbox into the current document. A Word textbox
can be used to create complex layouts, and position blocks of text anywhere on
the document.
Before calling this method, you need to set up several properties, as shown
in the example code above. This lets you set up
exactly how the TextBox will be drawn when you finally call the
InsertTextbox method.
The
self.Textbox.TextOrientation property
can be set to any equate listed
here.
The
self.Textbox.ZOrder property
can be set to any equate listed
here.
- NOTE: The self.Textbox.BorderColor
and self.Textbox.TextColor properties can either be standard clarion
color equates (as shown above), or RGB color values, e.g. 0D7D7D7H.
- NOTE: You must
either set the self.Textbox.XPos property or the self.Textbox.BoxAlignment property. There is no point in setting both.
- NOTE: Once this
method has completed drawing the textbox, focus returns to your
document, at the line immediately above where the textbox was drawn. If there is no line in your document above the textbox, focus will stay on /
in the textbox. Call the NextLine method before calling this method to ensure that focus returns
to your "document" once InsertTextbox completes, e.g.
MyWord.NextLine
( )
! set up properties, as shown above
MyWord.InsertTextbox ('Hello World')
Return Values
Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.Textbox.BoxAlignment = oiw:ShapeCenter
MyWord.Textbox.YPos = 153
MyWord.Textbox.Width = 200
MyWord.Textbox.Height = 50
MyWord.Textbox.ShowBorders = true
MyWord.Textbox.BorderColor = color:yellow
MyWord.Textbox.BorderWidth = '5'
MyWord.Textbox.TextFont = 'Arial'
MyWord.Textbox.TextSize = 20
MyWord.Textbox.TextColor = color:red
MyWord.Textbox.TextOrientation = oiw:TextOrientationHorizontal
MyWord.Textbox.TextAlignment = oiw:AlignParagraphRight
MyWord.Textbox.ZOrder = oiw:SendBehindText
MyWord.Textbox.MoveWithText = false
! once the properties are set we can now call the method...
MyWord.InsertTextbox ('Hello
world!') |
Italic
Italic ( byte pOption ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Makes the selected text italicized / not italicized.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
- pOption can be one of the following equates:
- oiw:ItalicOn
- oiw:ItalicOff
- oiw:ItalicToggle
Example
| Example |
MyWord.Italic (oiw:ItalicToggle)
TempByte = MyWord.Italic (oiw:ItalicToggle) |
Kill
Kill ( byte UnloadCOM=1 ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Closes any currently open documents (using the CloseDoc
method)
- Closes MS Word
- Kills the oiWord object and handles any cleaning up.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.Kill()
TempByte = MyWord.Kill() |
LinesToPoints
LinesToPoints ( string pLines ) ,string
Description
- Converts from lines to points. 1 lines = 12 points. The pLines parameter and the return
parameter are both strings however, as we figured this would make
your life easier to code (see examples above).
- See also
CentimetersToPoints,
InchesToPoints,
MillimetersToPoints,
PicasToPoints,
PixelsToPoints,
PointsToCentimeters,
PointsToInches,
PointsToLines,
PointsToMillimeters,
PointsToPicas, and
PointsToPixels.
Example
| Example |
loc:Points = MyWord.LinesToPoints(5)
MyWord.Update(oiw:PageLeftMargin, MyWord.LinesToPoints(5))
|
MailMergeEmail
MailMergeEmail(string pAddressField,<string
pSubject>,long pHighlightMergeFields=0,long pMailFormat=0),long,proc
Description
- Starts a Mail Merge Email process, i.e. sends the mail merge
document as an email to each
recipient in the list of the datasource file.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were reported.
Parameters
| Parameters |
|
pAddressField | The label of the
datasource field that contains the EmailAddress |
|
pSubject |
The subject to use in the email subject (cannot vary for each email) |
|
pHighlightMergeFields |
Set if you want to highlight the Merge Fields |
|
pMailFormat |
Set if you want the format to be HTML, or 0 for plain text (by
default). |
Example
| Example |
|
MyWord.MailMergeEmail('Email_Address','Test
HTML') |
See also
Using Mail Merge
MailMergePrint
MailMergePrint(<string pReserved>,long
pHighlightMergeFields=0),long,proc
Description
- Starts a Mail Merge Print process, i.e. sends the mail merge
document as a printout for each
recipient in the list of the datasource file.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were reported.
Parameters
| Parameters |
|
pReserved | Reserved for future use. |
|
pHighlightMergeFields |
Set if you want to highlight the Merge Fields in the printed
documents. |
Example
| Example |
|
MyWord.MailMergeEmail('') |
See also
Using Mail Merge
MailMergeInsertField
MailMergeInsertField(string pFieldName,long pPosition=0),long,proc
Description
- Inserts one of the data source fields into the Document.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were reported.
Parameters
| Parameters |
|
pFieldName | The label of the
datasource field that must be inserted into the document. |
|
pPosition |
If not zero, performs a selection to place the field in the
document. |
Example
| Example |
|
MyWord.MailMergeInsertField('First_Name') |
See also
Using Mail Merge
MailMergeRun (obsolete - use
MailMergeEmail)
MailMergeRun ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Starts a Mail Merge process.
- This method calls the MailMergeUpdate method before the actual merge begins.
- Returns true (1) is no problems were reported.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.MailMergeRun()
TempByte = MyWord.MailMergeRun() |
See also
Using Mail Merge
MailMergeSetDataSource
MailMergeSetDataSource(string DataSourceName,<string
pReservedForLaterUse>,<string pReservedForLaterUse2>),byte,proc
Description
- The method can be called to convert an existing Word document to a
MailMerge document, or to reset a current Mail Merge document to use a
different Datasource. In both instances, the document must exist, and be
open in word. The Datasource must also exist. When you create and save a Mail Merge document, it stores the path
to its Data Source. If this path changes (e.g. when you ship)
the Word document will no longer be able to open the Data Source.
This method enables you to set the Data Source path at run-time, which
enables you to get around this problem (as shown in the example
below).
- Returns true (1) if no problems were reported.
Example
| Example |
| MyWord.MailMergeSetDataSource ( (longpath() &
'\Addresses.csv'))
|
See also
Using Mail Merge
MillimetersToPoints
MillimetersToPoints ( string pMillimeters ) ,string
Description
- Converts from millimeters to
points. 1 mm = 2.85 points. The pMillimeters
parameter and the return parameter are both strings however, as we
figured this would make your life easier to code (see examples
above).
- See also
CentimetersToPoints,
InchesToPoints,
LinesToPoints,
PicasToPoints,
PixelsToPoints,
PointsToCentimeters,
PointsToInches,
PointsToLines,
PointsToMillimeters,
PointsToPicas, and
PointsToPixels.
Example
| Example |
loc:Points = MyWord.MillimetersToPoints(10)
MyWord.Update(oiw:PageLeftMargin, MyWord.MillimetersToPoints(1.10)) |
MoveDown
MoveDown ( byte pUnit=oiw:UnitLine, long pCount=1, byte pExtend=oiw:Move
) ,byte,proc
Description
- Has the same effect on your document as if you pressed the "down
arrow" key on the keyboard.
- The pExtend parameter can be either oiw:Move or oiw:Extend
- Returns true (1) is no problems were reported.
Example
| Example |
| MyWord.MoveDown() ! move down one line |
MoveLeft
MoveLeft ( byte pUnit=oiw:UnitCharacter, long pCount=1, byte pExtend=oiw:Move
) ,byte,proc
Description
- Has the same effect on your document as if you pressed the "left
arrow" key on the keyboard.
- The pExtend parameter can be either oiw:Move or oiw:Extend
- Returns true (1) is no problems were reported.
Example
| Example |
| MyWord.MoveLeft() ! move left one character |
MoveRight
MoveRight ( byte pUnit=oiw:UnitCharacter, long pCount=1, byte pExtend=oiw:Move
) ,byte,proc
Description
- Has the same effect on your document as if you pressed the "right
arrow" key on the keyboard.
- The pExtend parameter can be either oiw:Move or oiw:Extend
- Returns true (1) is no problems were reported.
Example
| Example |
| MyWord.MoveRight() ! move right one character |
MoveUp
MoveUp ( byte pUnit=oiw:UnitLine, long pCount=1, byte pExtend=oiw:Move
) ,byte,proc
Description
- Has the same effect on your document as if you pressed the "up
arrow" key on the keyboard.
- The pExtend parameter can be either oiw:Move or oiw:Extend
- Returns true (1) is no problems were reported.
Example
| Example |
| MyWord.MoveUp() ! move up one line |
NewDoc
NewDoc ( <string TemplateName> ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Creates a new document
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
- If you don't pass a TemplateName parameter, MS Word will use the
"normal.dot" template, which is standard behaviour.
If you do pass a template name, the full path to the ".dot"
file must be passed, unless the ".dot" file is in the default
template directory.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.NewDoc()
TempByte = MyWord.NewDoc()
MyWord.NewDoc ('MyTemplate.dot') ! assumes system default template directory
MyWord.NewDoc (longpath() & '/templates/MyTemplate.dot') |
NextLine
NextLine ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Moves to the next line within the document. Same as pressing
the "Enter" button from within MS Word.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.NextLine()
TempByte = MyWord.NextLine() |
OpenDoc
OpenDoc ( string pFileName, byte pReadOnly=false, byte pAddToRecentFiles=false,
<string pPassword> ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Opens an existing document
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
- ( Seems to be a problem under Win
XP / Office XP if the datasource is not in the original folder... )
Example
| Example |
MyWord.OpenDoc('c:\test.doc')
TempByte = MyWord.OpenDoc('c:\test.doc') |
OpenFooter
OpenFooter ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Makes the footer section of the currently open document "active",
so that you can work on / in it.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
| MyWord.OpenFooter() |
OpenHeader
OpenHeader ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Makes the header section of the currently open document "active",
so that you can work on / in it.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
| MyWord.OpenHeader() |
PageSetup
PageSetup (string pSetting, string pValue) ,byte,proc
Description
Allows the Page Setup attributes to be set for the current document (such
as left margin, bottom margin, and paper size). Sizes are passed in points
unless otherwise specified (see the notes below for the methods provided to
convert units). For values than can be either True or False
oi:True (-1) or
oi:False(0) must be
passed.
Passing Clarion style Boolean values will result in incorrect behaviour.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| string pSetting | A string specifying the settings to modify. Can be one of
the following values: |
| Name | Description |
| 'BookFoldPrinting' | oi:True for Microsoft Word to print a document in a series
of booklets so the printed pages can be folded and read as a
book. Must be oi:True or oi:False. |
| 'BookFoldPrintingSheets' | A Long which represents the number of
pages for each booklet. |
| 'BookFoldRevPrinting' | oi:True for
Microsoft Word to reverse the printing order for book fold printing of
bidirectional or Asian language documents. Must be oi:True or oi:False. |
| 'BottomMargin' | The distance (in points) between the bottom edge of the
page and the bottom boundary of the body text. |
| 'CharsLine' | The number of characters per line in the document grid. |
| 'DifferentFirstPageHeaderFooter' | True if a different header or footer is used on the
first page. Can be oi:True or oi:False. |
| 'FirstPageTray' | The paper tray to use for the first page
of a document or section. May be one of the following
values:oiw:PrinterAutomaticSheetFeed equate(7)
oiw:PrinterDefaultBin equate(0)
oiw:PrinterEnvelopeFeed equate(5)
oiw:PrinterFormSource equate(15)
oiw:PrinterLargeCapacityBin equate(11)
oiw:PrinterLargeFormatBin equate(10)
oiw:PrinterLowerBin equate(2)
oiw:PrinterManualEnvelopeFeed equate(6)
oiw:PrinterManualFeed equate(4)
oiw:PrinterMiddleBin equate(3)
oiw:PrinterOnlyBin equate(1)
oiw:PrinterPaperCassette equate(14)
oiw:PrinterSmallFormatBin equate(9)
oiw:PrinterTractorFeed equate(8)
oiw:PrinterUpperBin equate(1)
|
| 'FooterDistance' | Distance (in points) between the footer and the bottom
of the page. |
| 'Gutter' | The amount (in points) of extra margin space added to
each page in a document or section for binding. |
| 'GutterPos' | Which side the gutter appears in a document. Must be one
of the following:oiw:GutterPosLeft equate(0)
oiw:GutterPosRight equate(2)
oiw:GutterPosTop equate(1)
|
| 'GutterStyle' | Qhether Microsoft Word uses gutters for the current
document based on a right-to-left language or a
left-to-right language:oiw:GutterStyleBidi equate(2)
oiw:GutterStyleLatin equate(-10)
|
| 'HeaderDistance' | The distance (in points) between the header and the top
of the page. |
| 'LayoutMode' | Returns or sets the layout mode for the current
document:
oiw:LayoutModeDefault equate(0)
oiw:LayoutModeGenko equate(3)
oiw:LayoutModeGrid equate(1)
oiw:LayoutModeLineGrid equate(2)
|
| 'LeftMargin' | The distance (in points) between the left edge of the
page and the left boundary of the body text. |
| 'LinesPage' | The number of lines per page in the document grid. |
| 'MirrorMargins' | True (oi:True) if the inside and outside margins of
facing pages are the same width, otherwise oi:False |
| 'OddAndEvenPagesHeaderFooter' | True (oi:True) if the specified PageSetup object has
different headers and footers for odd-numbered and
even-numbered pages, otherwise oi:False. |
| 'Orientation' | Returns or sets the orientation of the page:oiw:OrientPortrait equate(0)
oiw:OrientLandscape equate(1)
|
| 'OtherPagesTray' | The paper tray to be used for all but the first page of
a document or section:
oiw:PrinterAutomaticSheetFeed equate(7)
oiw:PrinterDefaultBin equate(0)
oiw:PrinterEnvelopeFeed equate(5)
oiw:PrinterFormSource equate(15)
oiw:PrinterLargeCapacityBin equate(11)
oiw:PrinterLargeFormatBin equate(10)
oiw:PrinterLowerBin equate(2)
oiw:PrinterManualEnvelopeFeed equate(6)
oiw:PrinterManualFeed equate(4)
oiw:PrinterMiddleBin equate(3)
oiw:PrinterOnlyBin equate(1)
oiw:PrinterPaperCassette equate(14)
oiw:PrinterSmallFormatBin equate(9)
oiw:PrinterTractorFeed equate(8)
oiw:PrinterUpperBin equate(1) |
| 'PageHeight' | The height of the page in points. |
| 'PageWidth' | The width of the page in points. |
| 'PaperSize' | The paper size:oiw:Paper10x14 equate(0)
oiw:Paper11x17 equate(1)
oiw:PaperA3 equate(6)
oiw:PaperA4 equate(7)
oiw:PaperA4Small equate(8)
oiw:PaperA5 equate(9)
oiw:PaperB4 equate(10)
oiw:PaperB5 equate(11)
oiw:PaperCSheet equate(12)
oiw:PaperCustom equate(41)
oiw:PaperDSheet equate(13)
oiw:PaperEnvelope10 equate(25)
oiw:PaperEnvelope11 equate(26)
oiw:PaperEnvelope12 equate(27)
oiw:PaperEnvelope14 equate(28)
oiw:PaperEnvelope9 equate(24)
oiw:PaperEnvelopeB4 equate(29)
oiw:PaperEnvelopeB5 equate(30)
oiw:PaperEnvelopeB6 equate(31)
oiw:PaperEnvelopeC3 equate(32)
oiw:PaperEnvelopeC4 equate(33)
oiw:PaperEnvelopeC5 equate(34)
oiw:PaperEnvelopeC6 equate(35)
oiw:PaperEnvelopeC65 equate(36)
oiw:PaperEnvelopeDL equate(37)
oiw:PaperEnvelopeItaly equate(38)
oiw:PaperEnvelopeMonarch equate(39)
oiw:PaperEnvelopePersonal equate(40)
oiw:PaperESheet equate(14)
oiw:PaperExecutive equate(5)
oiw:PaperFanfoldLegalGerman equate(15)
oiw:PaperFanfoldStdGerman equate(16)
oiw:PaperFanfoldUS equate(17)
oiw:PaperFolio equate(18)
oiw:PaperLedger equate(19)
oiw:PaperLegal equate(4)
oiw:PaperLetter equate(2)
oiw:PaperLetterSmall equate(3)
oiw:PaperNote equate(20)
oiw:PaperQuarto equate(21)
oiw:PaperStatement equate(22)
oiw:PaperTabloid equate(23) |
| 'RightMargin' | The distance (in points) between the right edge of the
page and the right boundary of the body text. |
| 'SectionDirection' | The reading order and alignment for the specified
sections:oiw:SectionDirectionLtr equate(1)
oiw:SectionDirectionRtl equate(0)
|
| 'SectionStart' | The type of section break for the specified object.oiw:SectionContinuous equate(0)
oiw:SectionEvenPage equate(3)
oiw:SectionNewColumn equate(1)
oiw:SectionNewPage equate(2)
oiw:SectionOddPage equate(4) |
| 'SuppressEndnotes' | If oi:True endnotes are printed at the end of the next
section that doesn't suppress endnotes. Must be oi:True or
oi:False |
| 'TopMargin' | Returns or sets the distance (in points) between the top
edge of the page and the top boundary of the body text. |
| 'TwoPagesOnOne' | oi:True if Microsoft Word prints the specified document two
pages per sheet. Must be oi:True or oi:False |
| 'VerticalAlignment' | The vertical alignment of text on each page in a
document or section:oiw:AlignVerticalBottom equate(3)
oiw:AlignVerticalCenter equate(1)
oiw:AlignVerticalJustify equate(2)
oiw:AlignVerticalTop equate(0) |
| Parameter |
Description |
| string pValue | The value to set the passed setting to. See the Settings
descriptions above for valid values for each setting. |
Returns
True (1) if successful, or False (0) for failure. The
ErrorTrap
method will be called with error information in the event of a failure.
Notes
Important: For values than
can be either True or False,
oi:True (-1) or
oi:False (0)must be passed.
Word uses Points to specify sizes, and OfficeInside
provides methods to convert various units to points (and vice versa). See:
Paste
Paste ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Pastes from the clipboard to the current selection / cursor position
within a Word document.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.Paste()
TempByte = MyWord.Paste() |
PicasToPoints
PicasToPoints ( string pPicas ) ,string
Description
- Converts from picas to points. 1 pica = 12 points. ThepPicas
parameter and the return parameter are both strings however, as we
figured this would make your life easier to code (see examples above).
- See also
CentimetersToPoints,
InchesToPoints,
LinesToPoints,
MillimetersToPoints,
PixelsToPoints,
PointsToCentimeters,
PointsToInches,
PointsToLines,
PointsToMillimeters,
PointsToPicas, and
PointsToPixels.
Example
| Example |
loc:Points = MyWord.PicasToPoints(8)
MyWord.Update(oiw:PageLeftMargin, MyWord.PicasToPoints(8))
|
PixelsToPoints
PixelsToPoints ( string pPixels, byte pVertical=false ) ,string
Description
- Converts from pixels to points. ThepPixels
parameter and the return parameter are both strings however, as we
figured this would make your life easier to code (see examples
above).
- The pVertical parameter can be used to specify whether
you want to convert vertical pixels (if passed as true) or
horizontal pixels (if omitted or passed as false).
- See also
CentimetersToPoints,
InchesToPoints,
LinesToPoints,
MillimetersToPoints,
PicasToPoints,
PointsToCentimeters,
PointsToInches,
PointsToLines,
PointsToMillimeters,
PointsToPicas, and
PointsToPixels.
Example
| Example |
loc:Points = MyWord.PixelsToPoints(15)
MyWord.Update(oiw:PageLeftMargin, MyWord.PixelsToPoints(15))
|
PointsToCentimeters
PointsToCentimeters ( string pPoints ) ,string
Description
- Converts from points to
centimeters. 1 cm = 28.35 points. The pPoints
parameter and the return parameter are both strings however, as we
figured this would make your life easier to code (see examples
above).
- See also
CentimetersToPoints,
InchesToPoints,
LinesToPoints,
MillimetersToPoints,
PicasToPoints,
PixelsToPoints,
PointsToInches,
PointsToLines,
PointsToMillimeters,
PointsToPicas, and
PointsToPixels.
Example
| Example |
loc:Points = MyWord.PointsToCentimeters(6)
MyWord.Update(oiw:PageLeftMargin, MyWord.PointsToCentimeters(6))
|
PointsToInches
PointsToInches ( string pPoints ) ,string
Description
- Converts from points to inches. 1 inch = 72 points. The pPoints parameter and the return
parameter are both strings however, as we figured this would make
your life easier to code (see examples above).
- See also
CentimetersToPoints,
InchesToPoints,
LinesToPoints,
MillimetersToPoints,
PicasToPoints,
PixelsToPoints,
PointsToCentimeters,
PointsToLines,
PointsToMillimeters,
PointsToPicas, and
PointsToPixels.
Example
| Example |
loc:Points = MyWord.PointsToInches(14)
MyWord.Update(oiw:PageLeftMargin, MyWord.PointsToInches(14))
|
PointsToLines
PointsToLines ( string pPoints ) ,string
Description
- Converts from points to lines. 1 lines = 12 points. The pPoints parameter and the return
parameter are both strings however, as we figured this would make
your life easier to code (see examples above).
- See also
CentimetersToPoints,
InchesToPoints,
LinesToPoints,
MillimetersToPoints,
PicasToPoints,
PixelsToPoints,
PointsToCentimeters,
PointsToInches,
PointsToMillimeters,
PointsToPicas, and
PointsToPixels.
Example
| Example |
loc:Points = MyWord.PointsToLines(8)
MyWord.Update(oiw:PageLeftMargin, MyWord.PointsToLines(8))
|
PointsToMillimeters
PointsToMillimeters ( string pPoints ) ,string
Description
- Converts from points to millimeters. 1 mm = 2.835 points. The
pPoints parameter and the return
parameter are both strings however, as we figured this would make
your life easier to code (see examples above).
- See also
CentimetersToPoints,
InchesToPoints,
LinesToPoints,
MillimetersToPoints,
PicasToPoints,
PixelsToPoints,
PointsToCentimeters,
PointsToInches,
PointsToLines,
PointsToPicas, and
PointsToPixels.
Example
| Example |
loc:Points = MyWord.PointsToMillimeters(14)
MyWord.Update(oiw:PageLeftMargin, MyWord.PointsToMillimeters(14))
|
PointsToPicas
PointsToPicas ( string pPoints ) ,string
Description
- Converts from points to picas. 1 pica = 12 points. The
pPoints parameter and the return
parameter are both strings however, as we figured this would make
your life easier to code (see examples above).
- See also
CentimetersToPoints,
InchesToPoints,
LinesToPoints,
MillimetersToPoints,
PicasToPoints,
PixelsToPoints,
PointsToCentimeters,
PointsToInches,
PointsToLines,
PointsToMillimeters, and
PointsToPixels.
Example
| Example |
loc:Points = MyWord.PointsToPicas(12)
MyWord.Update(oiw:PageLeftMargin, MyWord.PointsToPicas(12))
|
PointsToPixels
PointsToPixels ( string pPoints, pVertical=false ) ,string
Description
- Converts from points to pixels. The pPoints parameter and the return
parameter are both strings however, as we figured this would make
your life easier to code (see examples above).
- The pVertical parameter can be used to specify whether
you want to convert vertical pixels (if passed as true) or
horizontal pixels (if omitted or passed as false).
- See also
CentimetersToPoints,
InchesToPoints,
LinesToPoints,
MillimetersToPoints,
PicasToPoints,
PixelsToPoints,
PointsToCentimeters,
PointsToInches,
PointsToLines,
PointsToMillimeters, and
PointsToPicas.
Example
| Example |
loc:Points = MyWord.PointsToPixels(13)
MyWord.Update(oiw:PageLeftMargin, MyWord.PointsToPixels(13))
|
PrintMe
PrintMe (<string
pPages>, byte pRange=oiw:PrintAllDocument, long pCopies=1,
byte pPageType=oiw:PrintAllPages, byte pBackground=false,
<string pPrinterName>) ,byte,proc
Description
Prints the currently loaded document. This method has been
replaced by the PrintOut(), which expands the supported options and is currently
in Beta (see below).
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| The pPages parameter holds the page numbers / ranges to be
printed. If you do not pass a value in this parameter, a value
of "print everything" is implied, but not passed.
(See "notes" below). Valid examples for this
parameter include: |
|
| The pRange parameter can be one of the following values: |
- oiw:PrintAllDocument (default)
- oiw:PrintSelection
- oiw:PrintCurrentPage
- oiw:PrintFromTo (not supported, use pPages instead)
- oiw:PrintRangeOfPages (see notes below)
|
| The pCopies parameter is not supported by this method, use PrintOut()
instead. | |
| The pPageType parameter can be one of the following values: |
- oiw:PrintAllPages
(default)
- oiw:PrintOddPagesOnly
- oiw:PrintEvenPagesOnly
|
| The pBackground parameter determines whether this method returns
before or after the document has actually been sent to the
printer. This is very useful. Passing this parameter as
"true" (1) will make the method return faster (as it does
not wait for confirmation that the document has been sent to the
printer), but you need to consider the implications of this.
One implication is that calling MyWord.Kill might cause MS Word to
show the "Word is currently printing. Quitting Word will
cancel all pending jobs" warning. Passing this parameter
as "false" (0) guarantees that the document has been sent
to the printer before the PrintMe method returns, solving the
problem (at the cost of a slight delay when you call the method). | |
| The pPrinterName parameter can be used to specify a printer other
than the default printer, for example: |
MyWord.PrintMe ('1',,,,,'PDF-XChange
3.0') |
Notes
In order for the pPages parameter to work, pRange
needs to be
oiw:PrintRangeOfPages.
If you pass a value in pPages, and also pass anything other than
oiw:PrintRangeOfPages
in pRange, we will simply ignore what you pass in pRange.
We do this so that the following code will work, even though
pRange is going to default to
oiw:PrintAllDocument, which wouldn't ordinarily work:
MyWord.PrintMe ( '3,4,7-8' )
If you're wanting to print a document to a printer
other than
the system default printer, the "safest" way to do this
seems to be it is done in the "
Two Printers"
example. Notes can be found in that example.
Examples
| Example |
TempByte = MyWord.PrintMe ()
MyWord.PrintMe ('2,4,5-8') ! oiw:PrintRangeOfPages implied (see
"Notes")
MyWord.PrintMe ('2,4', oiw:PrintRangeOfPages)
MyWord.PrintMe ( ,oiw:PrintCurrentPage)
MyWord.PrintMe ( ,oiw:PrintSelection)
MyWord.PrintMe ( ,,,oiw:PrintOddPagesOnly)
MyWord.PrintMe ( ,,2)
MyWord.PrintMe ('1',,,,,'Lexmark 3200') |
PrintOut
PrintOut (*oiwPrintProperties printSettings, string
printerName)
Description
The PrintOut method expand on the simple PrintMe() method
and exposes all the properties supports by Word. The oiwPrintProperties group
type is provided to allow the setting to be easily set and passed.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
Example |
| *oiwPrintProperties printSettings |
A oiwPrintProperties group that contains the settings to be
used for printing. See below for a description of the group type and fields.
This is a TYPE'd group and can be used to create your own PrintSettings groups
as follows: |
myPrintSettings
group(oiwPrintProperties)
end |
| string printName |
The name of the printer to use for printing. See the
PrintOut example, which uses the oiUtil class to enumerate all printers on the
system. |
|
Return Values
Returns 1 for success and zero if the COM interface
encountered an error.
Data Types
| oiwPrintProperties Type Fields |
| Name | Type |
Description |
| background | long | Set to
True to have the code to execute continue
while Microsoft Word prints the document. |
| pAppend | long | Set to True to append the specified document to the
file name specified by the OutputFileName argument.
False to overwrite the contents of OutputFileName. |
| pRange | long | The page range. Can be any
oiw:PrintOutRange
constant:
oiw:PrintAllDocument equate(0)
oiw:PrintSelection equate(1)
oiw:PrintCurrentPage equate(2)
oiw:PrintFromTo equate(3)
oiw:PrintRangeOfPages equate(4) |
| outputFileName | cstring(256) | If PrintToFile is
True, this argument
specifies the path and file name of the output file. |
| pFrom | long | The starting page number when Range is set to
oiw:PrintFromTo. |
| pTo | long | The ending page number when Range is set to
oiw:PrintFromTo. |
| pItem | long | The item to be printed. Can be any
oiw:PrintOutItem constant:
oiw:PrintDocumentContent equate(0)
oiw:PrintProperties equate(1)
oiw:PrintMarkup
equate(2)
oiw:PrintComments
equate(2)
oiw:PrintStyles
equate(3)
oiw:PrintAutoTextEntries equate(4)
oiw:PrintKeyAssignments equate(5)
oiw:PrintEnvelope
equate(6)
oiw:PrintDocumentWithMarkup equate(7) |
| copies | long | The number of copies to be printed. |
| pages | cstring(1024) | The page numbers and page ranges to be printed, separated
by commas. For example, "2, 6-10" prints page 2 and pages 6
through 10. |
| pageType | | The type of pages to be printed. Can be any
oiw:PrintOutPages constant:
oiw:PrintAllPages
equate(0)
oiw:PrintOddPagesOnly equate(1)
oiw:PrintEvenPagesOnly equate(2) |
| printToFile | | True to send printer instructions to a file. Make
sure to specify a file name with OutputFileName. |
| collate | | When printing multiple copies of a document,
True
to print all pages of the document before printing the next copy. |
| FileName | | The path and file name of the document to be printed. If
this argument is omitted, Word prints the active document.
(not tested) |
| activePrinterMacGX | | Not supported on the Windows platform. |
| manualDuplexPrint | |
True to print a two-sided document on a printer
without a duplex printing kit. If this argument is
True,
the PrintBackground and
PrintReverse
properties are ignored. This argument may not be available
to you, depending on the language support that you’ve
selected or installed. |
| printZoomColumn | | The number of pages you want Word to fit horizontally on
one page. Can be 1, 2, 3, or 4. Use with the PrintZoomRow
argument to print multiple pages on a single sheet. |
| printZoomRow | | The number of pages you want Word to fit vertically on one
page. Can be 1, 2, or 4. Use with the PrintZoomColumn
argument to print multiple pages on a single sheet. |
| printZoomPaperWidth | | The width to which you want Word to scale printed pages,
in twips (20 twips = 1 point; 72 points = 1 inch). |
| printZoomPaperHeight | | The height to which you want Word to scale printed pages,
in twips (20 twips = 1 point; 72 points = 1 inch). |
PrintPreview
PrintPreview ( ) ,byte or ( byte pOption ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Print Previews the current document, or establishes whether the
current document is being previewed.
Example
| Example |
TempByte = MyWord.PrintPreview ()
( TempByte will be 1 if on, 0 if not )
MyWord.PrintPreview (1) ! turn print preview
on
MyWord.PrintPreview (0) ! turn print preview off
MyWord.PrintPreview (2) ! toggle print preview
TempByte = MyWord.PrintPreview (1) ! turn print
preview on
! TempByte will return 1 if passed, 0 if an error occurred |
Protect
Protect (long
protectionType, string pPassword),long
Description
Enables document protection. This limits what changes may be made to the document unless
document protection is turned off. If a password is specified then that
password must be used to turn document protection off. Once you enabled
document protection the same limits that apply to the end user also
apply to other methods called. For example if you enabled document
protection and set the document to Read Only, you will not be able to
modify the document by calling any of the oiWord methods until oiWord.
Unprotect
is called to remove the protection.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| long protectionType |
Type of protection to enabled. Can be one of the following values:
- oiw:AllowOnlyComments - Only comments can be added or edited
- oiw:AllowOnlyFormFields - Only form fields may be have their values edited.
- oiw:AllowOnlyReading - Document is read only, no changes may be made
- oiw:AllowOnlyRevisions - Only revisions may be made
- oiw:NoProtection - No protection (the same as
calling Unprotect()).
|
| string pPassword |
The password used to protect the document. This password will be needed to
remove the protection. A blank string may be specified, which means that the
protection can be removed without setting any password. |
Return Values
Returns 1 for success and zero for failure.
Example
| Example |
MyWord1.Protect(oiw:AllowOnlyComments,
'capesoft')
MyWord1.Protect(oiw:AllowOnlyFormFields, 'capesoft')
MyWord1.Protect(oiw:AllowOnlyReading, 'capesoft')
MyWord1.Protect(oiw:AllowOnlyRevisions, 'capesoft')
MyWord1.Unprotect('capesoft') |
Redo
Redo ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Opposite to the "Undo" method.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.Redo()
TempByte = MyWord.Redo() |
ReplaceText
ReplaceText (string
pFindText, string pReplaceText, byte pReplaceAll=false), byte, proc
Description
Search and replace method, locates a string in the document
and replaces it with the specified string. This method searches the currently
loaded document for the text you pass as the
pFindText
parameter, and then replaces that text with the text which you pass
as the
pReplaceText parameter. The
pReplaceAll parameter determines whether the first
instance the word / text is replace, or whether all instances are
replaced.
Important: Word limits the
size of the strings being replaced and the replacement text to 256 characters.
There are two ways of replacing strings larger than 256 characters:
- If your replacement string contains more than 256 characters use the
FindText method to find the string and the call the
InsertText method to replace it with your own string. You can to replace all
instances by looping and calling FindText and replacing each instance until the
FindText method it fails (returns zero), indicating that the string no longer
exists in the document.
-
Simply put your LargeString on the clipboard and call
the ReplaceText method with the pRelaceText set to '^c':
MyWord.ReplaceText('LookFor',
'^c',
True)
The 2-character string '^c' will be
interpreted by Word as the Paste command. This also has the advantage of
supporting inserting RTF formatting text into Word (the Paste command is the
only way to insert RTF formatting text directly into a Word document)
Note: Replacement text inherits the formatting of the
text it replaces in the document. For example, if you replace the
string "abc" with "xyz," occurrences of "abc" with bold formatting
are replaced with the string "xyz" with bold formatting. This
also applies to case, in that if you replace "acb" with "xyz" you
will get "xyz", but if you replace "ABC" with "xyz" you will in fact
get "XYZ". This is actually pretty useful once you understand
how it works, in that you can lay out the same search string in a
document, multiple times, and each string can have its own
formatting (case, bold, underlined etc) which is preserved when you
replace.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| string pFindText | The text to find in the
document. This will be replace by the pReplaceText string if it is found. |
| string pReplaceText | The text to replace the
pFindText string with |
| byte pReplaceAll | An optional parameter
specifying that all instances of the pFindText string in the document should
be replaced by the pReplaceTextString. The default is false (only replace
the first occurrence). Setting this to true (1) will replace all
occurrences. |
Return Values
Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced (Note: A return
value of
true does not indicate that any text was actually
replaced. In other words, if the text you are searching for is not
found, the method can still return
true).
Example
| Example |
MyWord1.ReplaceText('Cape', 'Soft')
MyWord1.ReplaceText('Cape', 'Soft',
true)
MyWord1.ReplaceText(searchString,
replaceString) |
RestoreSnapShotOfWindowPos
RestoreSnapShotOfWindowPos ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- This method is used in conjunction with the
TakeSnapShotOfWindowPos method, and is used to restore the window
size and state of an Office application once your app has finished
using it. The templates will generate code immediately before
the Kill method call to call this method, so if you're using the
templates you do not need to worry about this method as it will be
called automatically.
Example
| Example |
| MyWord.RestoreSnapShotOfWindowPos () |
RunMacro
RunMacro (string pMacroName,<string pParameter1>,<string pParameter2>,<string
pParameter3>,<string pParameter4>,<string pParameter5>,<string
pParameter6>,<string pParameter7>,<string pParameter8>,<string
pParameter9>,<string pParameter10>) ,byte,proc
Description
- Runs the specified macro. The specified macro must already exist in
the instance of word.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
|
TempByte = MyWord.RunMacro('MyMacro') |
Save
Save ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Saves the current document, must have already been saved using the
SaveAs method, or the document will not
have a valid file name to "save to".
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.Save()
TempByte = MyWord.Save() |
SaveAs
SaveAs ( <string pFileName>, long pFileFormat=oiw:SaveFormatDocumentDefault, <string
pOpenPassword>, <string pEditPassword> ) ,byte,proc
Description
Saves the current document. If the FileName parameter is passed
as an empty string (''), or is omitted, then a normal
Save
will be done. The
pFileFormat parameter can be one of the values
(equates) listed below.
Important:
- As a result of changes to the behaviour of Word 2007, using
oiw:FormatDocument
as the pFileFormat now implies the old DOC
format. This changes the behaviour of existing code, and as a result if you
specify the incorrect file extension (.docx), you may be left with a
document that does not open in Word. The default value for the pFormat
parameter has been changed to
oiw:SaveFormatDocumentDefault. Because
oiw:FormatDocumentDefault doesn't exist in
older version of Word, OfficeInside will automatically detect the version of
Word being used, and use the correct document format for that version (oiw:FormatDocument
for Word 2003 and earlier and oiw:FormatDocumentDefault for Word 2007 and
later).
- We recommend not specifying a file extension, unless you are certain of
the format that the document will be in. Word will automatically append the
correct file extension. The GetFileName() method can be called once the file
is saved to get the resultant file name. Alternatively before calling
SaveAs() the GetOfficeVersion() method can be called to get the version of
Office, and the file format and extension then chosen appropriately.
- The old equates, such as oiw:SaveFormat_EncodedText should be considered
deprecated.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| pFileName | The name and path of the file to open. If no path is
specified, then OfficeInside will prefix the file name with the current
application path. |
| pFileFormat |
Word 2007 and later changes the meaning of a number of equates. In these cases the new version of the
equate is show in bold below and highlighted
oiw:FormatDocument equate(0) ! Microsoft Office Word format.
oiw:FormatDocument97 equate(0) ! Microsoft Word 97 document format.
oiw:FormatTemplate equate(1) ! Word template format.
oiw:FormatTemplate97 equate(1) ! Word 97 template format.
oiw:FormatText equate(2) ! Microsoft Windows text format.
oiw:FormatTextLineBreaks equate(3) ! Windows text format with line breaks preserved.
oiw:FormatDOSText equate(4) ! Microsoft DOS text format.
oiw:FormatDOSTextLineBreaks equate(5) ! Microsoft DOS text with line breaks preserved.
oiw:FormatRTF equate(6) ! Rich text format (RTF).
oiw:FormatEncodedText equate(7) ! Encoded text format.
oiw:FormatUnicodeText equate(7) ! Unicode text format.
oiw:FormatHTML equate(8) ! Standard HTML format.
oiw:FormatWebArchive equate(9) ! Web archive format.
|
Available in Word 2007 and later
|
oiw:FormatFilteredHTML equate(10) ! Filtered HTML format.
oiw:FormatXML equate(11) ! Extensible Markup Language (XML) format.
oiw:FormatDocumentDefault equate(16) ! Default document(.docx for Word 2007 and up)
oiw:FormatPDF equate(17) ! PDF format.
oiw:FormatXMLDocument equate(12) ! XML document format.
oiw:FormatXMLDocumentMacroEnabled equate(13) ! XML document format with macros enabled.
oiw:FormatXMLTemplate equate(14) ! XML template format.
oiw:FormatXMLTemplateMacroEnabled equate(15) ! XML template format with macros enabled.
oiw:FormatXPS equate(18) ! XPS format. |
| pOpenPassword | Optional parameter that specifies a password to be used
to protect the document. If this is passed, then the document will required this
password in order to be opened. Can be used in conjunction with the
pEditPassword parameter. |
| pEditPassword | Optional parameter that specifies a password that allows
the document to be edited. If this is specified then the document can still be
opened without the password, however changes cannot be saved to the same
document (SaveAs can still be used to save to the a new document, but the
original file is treated as Read-Only). Can be used in conjunction with the
pOpenPassword parameter. |
Return Value
Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced, and
false (0) if an error occurs. In the event of an error occuring the ErrorTrap()
method is called with additional information.
Examples
| Example 1 |
| Use the default format, add default extension automatically In the
current app path. |
if WordDoc.SaveAs('mydocument')
savedFileName = WordDoc.GetFileName()
else
end |
| Example 2 |
| Get the version of Office installed, and pick a file name and extension
based on the version. Functionally identical to the approach in example 1. |
officeVersion = WordDoc.GetOfficeVersion()
if officeVersion
< 12
WordDoc.SaveAs('Document.doc', oiw:FormatDocument)
else
WordDoc.SaveAs('Document.docx', oiw:FormatDocumentDefault)
end |
| Example 3 |
| Identical to calling Save(). Prompts the user for a file name if the
file has not been saved already. |
if not WordDoc.SaveAs()
Message('Saving
the document failed')
end |
| Example 4 |
| Save with a password required to open the file |
|
WordDoc.SaveAs(LongPath
() & '\PasswordedDoc',
oiw:FormatDocumentDefault, 'openpassword')
|
| Example 5 |
| Save with a password required to open the file, and a password to edit
the document |
|
WordDoc.SaveAs(LongPath
() & '\PasswordedDoc', oiw:FormatDocumentDefault, '
openpassword', 'editpassword') |
RefreshScreen
RefreshScreen ()
Description
Redraws the screen. This method is useful when screen
updating (redrawing) has been turned off using the
SetScreenUpdating()
method. Turn screen updating off can provide
a small performance improvement for batch inserts etc. It is only recommended
in cases where the user does not have to see or interact with the
document. The same method can be used with the oiExcel object to
slightly improve performance. For Excel, a large performance increase
can be achieved when doing bulk updates by using the
SetCalculations method.
Note: There have been some
reports of this causing problems with documents that the user opens while this
setting is enabled. Considering how small the performance benefit of this option
is we suggest using it with caution and ensuring that RefreshScreen() is called
periodically and that screen updating is re-enabled once your are done.
Parameters
None
Return Value
Returns 1 if the function succeeds, and zero for
failure. If the function fails the ErrorTrap() method is called
with information relating to the error.
Example
| Example |
WordDoc.SetScreenUpdating(false)
WordDoc.RefreshScreen() |
SetBackground
SetBackground ( long pColor=0, <string pFileName> ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the background for the currently loaded document
- You cannot pass both a color and a filename, you must only pass
one or the other (as in the code examples above)
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.SetBackground ( ) ! no fill
MyWord.SetBackground (color:yellow) ! fill color
MyWord.SetBackground ( , 'c:\images\logo.jpg') ! fill image
|
SetFontColor
SetFontColor ( long FontColor ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the color for the currently selected text.
- Standard Clarion color equates can be used, as shown above.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.SetFontColor (COLOR:Green)
TempByte = MyWord.SetFontColor (COLOR:Green) |
SetFontName
SetFontName ( string FontName ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the font name (font).
Example
| Example |
MyWord.SetFontName ('Arial')
TempByte = MyWord.SetFontName ('Arial') |
SetFontSize
SetFontSize ( long FontSize ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the current font size.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.SetFontSize(14)
TempByte = MyWord.SetFontSize(18) |
SetPageView
SetPageView ( byte pPageView ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the view for the current page, to one of the following:
- oiw:NormalView
- oiw:OutlineView
- oiw:PrintView
- oiw:PrintPreview
- oiw:MasterView
- oiw:WebView
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.SetPageView (oiw:NormalView)
TempByte = MyWord.SetPageView (oiw:NormalView) |
SetParagraphFormatting
SetParagraphFormatting ( long pOption, string pValue, <string pValue2> ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the formatting for the currently selected paragraph.
- The pOption parameter can be one of the following
equates:
- oiw:LeftIndentation
- oiw:RightIndentation
- oiw:SpacingBefore
- oiw:SpacingAfter
- oiw:LineSpacing
- If you pass oiw:LineSpacing for the pOption
parameter, then the pValue parameter must be one of the
following equates:
- oiw:LineSpaceSingle
- oiw:LineSpace1pt5
- oiw:LineSpaceDouble
- oiw:LineSpaceAtLeast
- oiw:LineSpaceExactly
- oiw:LineSpaceMultiple
- If you pass oiw:LineSpaceExactly for the pValue parameter, you must specify the value you want to set the line
spacing to using the pValue2 parameter, as in the example
code above.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
- See also AlignCenter,
AlignJustify,
AlignLeft, AlignRight
Example
| Example |
MyWord.SetParagraphFormatting (oiw:SpacingBefore, 30)
MyWord.SetParagraphFormatting (oiw:LeftIndentation,
MyWord1.CentimetersToPoints(2))
MyWord.SetParagraphFormatting (oiw:LineSpacing, oiw:LineSpaceSingle)
MyWord.SetParagraphFormatting (oiw:LineSpacing, oiw:LineSpaceExactly,
18)
|
SetScreenUpdating
SetScreenUpdating (long updateScreen)
Description
This method allows screen updating (redrawing) to be turned off and on. Turn
screen updating off can provide a small performance improvement
for batch inserts etc. It is only recommended in cases where the
user does not have to see or interact with the document. The same
method can be used with the oiExcel object to slightly improve performance.
For Excel, a large performance increase can be achieved when doing
bulk updates by using the
SetCalculations method.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| long updateScreen | Set this to 1(true) to turn screen updating on, and to zero (false)
to turn screen updating off. |
Return Value
Returns 1 if the function succeeds, and zero for
failure. If the function fails the ErrorTrap() method is called
with information relating to the error.
Example
| Example |
WordDoc.SetScreenUpdating(false)
WordDoc.SetScreenUpdating(true) |
SetSelection
SetSelection ( long pSelectionStart=0, long pSelectionEnd=0 ) ,byte,proc
Description
- If no parameters are passed (i.e. pSelectionStart and pSelectionEnd
are passed as 0), the entire document is selected (equivalent to
Ctrl-A).
- If you do pass values is the parameters, the text from character
position pSelectionStart, to pSelectionEnd is selected.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.SetSelection () ! select everything
MyWord.SetSelection (10, 30) ! select from pos 10 to pos 30
|
OR:
SetSelection ( long pTableNumber=1, long
pColumnNumber, long pRowNumber ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Selects the contents of a cell within a table. If you have
more than one table in a document, you can specify which table with
the pTableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- If you pass 0 (zero) in both the pColumnNumber and the pRowNumber
parameters, then the entire table (not all the cells,
but the table itself) identified by pTableNumber is
selected. This can be used to copy an entire table for instance. If pColumnNumber
is 0, then the entire row is selected, and likewise if pRowNumber
is 0 then the entire column is selected.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.SetSelection (1, 3, 4) ! select
cell C4 in table 1
MyWord.SetSelection (1, 0, 0) ! select table 1
MyWord.SetSelection (2, 3, 0) ! select column 3 in table 2
MyWord.SetSelection (3, 0, 5) ! select row 5 in table 3 |
SetStyle
SetStyle (string pStyle) ,long,proc
Description
- This method should be called after SetSelection. This method will
apply the pStyle (the name of the style) to the currently selected text.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.SetSelection (10, 30) ! select from pos 10 to pos 30
MyWord.SetStyle ('Heading 1') ! Set the selection to use the Heading 1
style. |
See also
SetSelection
ShowMessage
ShowMessage ( string _pText, string _pCaption, string _pIcon, long _pID )
Description
There are times when it is helpful if Office Inside
displays a message, such as if an Office Application cannot be loaded or
a document which you try to open does not actually exist, or so on.
Because we know how frustrating it can be to have 3rdParty tools
displaying messages in your applications Office Inside has this method,
called
ShowMessage.
The way it works is as follows: If Office Inside needs to show a
message we call this method, rather than calling the Clarion
Message() or
Stop() function directly. Inside this
method (in our DLL) we call the Clarion
Message function.
The reason we do this is to give you a way to control which messages are
shown, and how they are shown. If you embed
code into the
ShowMessage method, before the parent call, then every time Office
Inside wants to show a message it will first run your code, then call
the message, giving you a chance to "tweak" this, as illustrated below:
| Example |
MyWord1.ShowMessage PROCEDURE (string
_pText, string _pCaption, string _pIcon, long _pID)
CODE
case
_pID
of oiw:Msg_Error_StartingWord
! no custom code
of
oiw:Msg_Confirm_SpellCheckComplete
message ('Well done! No spelling mistakes.')
return
of
oiw:Msg_Error_SpellCheckFailed
return
end
PARENT.ShowMessage(_pText, _pCaption, _pIcon, _pID)
|
Notes
Every time Office Inside wants to show a message it will call this
method, setting _pID to one of the equates listed
here.
In the code above my "custom" code (shown in red) tweaks
which messages I actually allow Office Inside, and which I
don't. If the message was to warn that MS Word could not be
started (_pID = oiw:Msg_Error_StartingWord), then I do nothing, so
Office Inside will show it's message as per default. If the
message is to tell the user that the Spell Check is now complete and
there were no problems, I've changed the default behavior by showing
my own message here, then returning before the parent call so that
Office Inside's message does not also show. If the message was
to warn that an error occurred during the Spell Check, I have decided
that the user should not see that message and simply return before the
parent call, so no message will be shown whatsoever. If you are
happy to let Office Inside show any messages (we are obviously careful
about what messages we show) then there is no need to put any code
into this embed point yourself. To change the icon shown in the
Office Inside messages use the
oi_ChangeDefaultShowMessageIcon
funciton.
ShowToolbar
ShowToolbar (long pToolbar ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets a MS Word toolbar to be visible. For
a list of valid equates which can be used, click here.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
|
MyWord.ShowToolbar
(oiw:ToolbarStandard) |
SetPrinter
SetPrinter(string printerName)
Description
Sets the printer for the current Word document. Also turns
off the display of print dialogs by calling the
SetAlerts
method automatically. This functionality is provide by the
PrintOut
method, so it not typically called directly.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| string printerName | The name of the printer. See the PrintOut example
application for an example of listing the installed printers. |
Return Values
Returns true for success and false for failure.
Examples
| Example |
| oiWord.SetPrinter(printerName) |
See Also
PrintOut
SetAlerts
SetAlerts (long alertLevel)
Description
Sets the alert level (whether Word displays dialogues).
Called automatically when PrintOut is used to allow automation of printing.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| string alertLevel | Can be one of the following levels:
oiw:AlertsNone(0), oiw:AlertsMessageBox(-2),
or oiw:AlertsAll(-1). |
Return Values
Returns true for success and false for failure.
Examples
| Example |
| oiWord.SetAlerts(oiw:AlertsNone) |
ScreenRefresh
ScreenRefresh()
Refreshes the screen when screen updating has been turned off using the SetScreenUpdating
method. Turning off screen updating when the window is hidden
or when doing bulk inserts can improve performance by a small amount.
Not that you need to call SetScreenUpdating to turn updating back
on before calling ScreenRefresh() to refresh the display.
Parameters
None
Return Values
None
Examples
| Example |
oiWord.SetScreenUpdating(true)
oiwWord.ScreenRefresh() |
See Also
SetScreenUpdating
SpellCheckString
SpellCheckString (*string
checkText, long silent=1, long htmlText=0), long, proc
Description
Note that the
template provides spell checking, and these methods are the underlying
code that is used. If you use the provided spell checking templates
you do not need to implemented these methods yourself.
Spell checks the passed string (
checkText) and allows the user to correct the
spelling, while providing suggestions (much like Word, Outlook Express etc. would).
Office Inside provides a Utility Template to add a Spell
Checking window to your application. This procedure (
oiShowSpellingSuggestions)
provides a user interface for spell checking. For each word that may
be misspelled this procedure calls the
SpellWord procedure, which is
generated into the procedure that you have added spell checking to.
You should call your
oiShowSpellingSuggestions
from the
SpellWord procedure
(copy the bold line below to before the parent call):
oiWord.SpellWord
Procedure (string pWord, *oiwWordsQ WordsQ, *long pCommand)
CODE
return(oiShowSpellingSuggestions(pWord, WordsQ, pCommand))
! Copy this
line
If you are using the Spell Checking template this can be done automatically by
the template.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| *string checkText | The string to spell check.
There should be sufficient room in this string for any corrections (the
corrected text may be longer than the passed text). |
| long silent | Determines if the procedure
displays a "Spell Checking Done" message box when spell checking of the
string is complete. The default value is 1, which would not display a
message, set this to zero in order to display the message. |
| long htmlText | Indicates that the passed text
comes from HTML and may contain HTML escape codes (such as ) and URL
encoded characters (such as %A1). You cannot pass HTML to this method, you
should pass HTML to the SpellCheckHTML method, this setting is only for specific characters
that occur in HTML. The default value is zero. This setting would
not typically be used unless you are replacing the
SpellCheckHtmlmethod with a version of your own and are passing the text portions
of the HTML, excluding any tags etc., to this method. |
Return Value
The function returns 1 for success or zero if an error occurred.
Example
| Example |
case
Choice(?SheetMailEdit)
of 1
orof 2
HtmlEditor.GetInfo()
if Len(HtmlEditor.html2Source)
> Len(htmlSource)
htmlSource = HtmlEditor.html2Source[1 :
Len(htmlSource)]
else
htmlSource = HtmlEditor.html2Source
end
WordSpell.SpellCheckHtml(htmlSource)
HtmlEditor.Update('Html2Source',
Clip(htmlSource))
of 3
WordSpell.SpellcheckString(textData)
Display(?textData)
end |
See Also
SpellWord,
SpellCheckString
SpellCheckHtml
SpellCheckHtml (*string
checkHtml, long silent=1)
Description
Note that the template provides spell checking, and these
methods are the underlying code that is used. If you use the provided
spell checking
templates you do not need to implemented these methods yourself.
Spell checks the passed string (
checkHtml) and allows the
user to correct the spelling, while providing suggestions (much like
Word, Outlook Express etc. would). This function is identical to the
SpellCheckString, except that it handles HTML content in the string.
HTML tags, JavaScript,
HTML escape codes and URL encoded characters are all ignored. This
method provides spell checking support for File Explorer.
Office Inside provides a Utility Template to add a Spell Checking window to your
application. This procedure (
oiShowSpellingSuggestions) provides a
user interface for spell checking. For each word that may be misspelled
this procedure calls the
SpellWord procedure, which is generated into
the procedure that you have added spell checking to. You should call
your
oiShowSpellingSuggestions from the
SpellWord procedure (copy the
bold line below to before the parent call):
oiWord.SpellWord PROCEDURE (string pWord, *oiwWordsQ WordsQ, *long pCommand)
CODE
return(oiShowSpellingSuggestions(pWord, WordsQ, pCommand))
If you are using the Spell Checking template this can be done automatically by
the template.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| *string checkHtml | The string to spell check.
There should be sufficient room in this string for any corrections (the
corrected text may be longer than the passed text). This string contains the
contents of an HTML file. For checking text rather than HTML call the
SpellCheckString method. |
| long silent | Determines if the procedure
displays a "Spell Checking Done" message box when spell checking of the
string is complete. The default value is 1, which would not display a
message, set this to zero in order to display the message. |
Return Value
The function returns 1 for success or zero if an error occurred.
Example
| Example |
case Choice(?SheetMailEdit)
of 1
orof 2
HtmlEditor.GetInfo()
if Len(HtmlEditor.html2Source)
> Len(htmlSource)
htmlSource = HtmlEditor.html2Source[1 :
Len(htmlSource)]
else
htmlSource = HtmlEditor.html2Source
end
WordSpell.SpellCheckHtml(htmlSource)
HtmlEditor.Update('Html2Source',
Clip(htmlSource))
of 3
WordSpell.SpellcheckString(textData)
Display(?textData)
end |
See Also
SpellWord,
SpellCheckHtml
SpellWord
SpellWord (string
pWord, *oiwWordsQ WordsQ, *long pCommand)
Description
This virtual method is called for each word that may be
incorrect when CheckSpelling is called. This method provides a place for embed
code to be added to display a spell checking user interface.
If you are using the Spell Checking template this can be done automatically by
the template.
oiWord.SpellWord PROCEDURE (string pWord, *oiwWordsQ WordsQ, *long pCommand)
CODE
return(oiShowSpellingSuggestions(pWord, WordsQ, pCommand))
We recommend using the oiShowSpellingSuggests method that
the templates provide and modifying it according to your specific needs.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| *string pWord | The word being spell checking
that may be incorrect |
| oiwWordsQ WordsQ | A list of spelling suggests that Word has
made to replace the current word |
Return Value
The action that is to be performed, which can be one of the
following values:
oiw:Replace (0)
oiw:Ignore (1)
oiw:AddToDictionary (2)
oiw:ReplaceAll (3)
oiw:IgnoreAll (4)
Example
| Example |
oiWord.SpellWord PROCEDURE (string pWord, *oiwWordsQ WordsQ, *long pCommand)
CODE
return(oiShowSpellingSuggestions(pWord, WordsQ, pCommand))
|
See Also
SpellCheckString,
SpellCheckHtml
TableAutoFormat
TableAutoFormat (longtableNumber, long tableStyle), long
Description
Formats the specified table using one of the styles
provided by Word. These styles apply formatting to both the table and
table contents. When new columns and rows are added the automatic
formatting may not be applied to them, in which case the
TableUpdateAutoFormatting
method may be called to apply the same formatting to any new rows and
columns.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| long tableNumber | The number of the table to
format. Word numbers the first table in the document as 1, and each
successive table increments that table number. Note that the tables are
numbered in the order that they occur in, not in the order that they were
added to the table, so if you have two tables and insert a new one between
them the last table is numbered 3, rather than 2. |
| long tableStyle | An equate that
specifies one of the build-in styles provided by Word. May be one of the
following values:
- oiw:TableFormatNone
- oiw:TableFormatSimple1
- oiw:TableFormatSimple2
- oiw:TableFormatSimple3
- oiw:TableFormatClassic1
- oiw:TableFormatClassic2
- oiw:TableFormatClassic3
- oiw:TableFormatClassic4
- oiw:TableFormatColorful1
- oiw:TableFormatColorful2
- oiw:TableFormatColorful3
- oiw:TableFormatColumns1
- oiw:TableFormatColumns2
- oiw:TableFormatColumns3
- oiw:TableFormatColumns4
- oiw:TableFormatColumns5
- oiw:TableFormatContemporary
- oiw:TableFormatElegant
- oiw:TableFormatGrid1
- oiw:TableFormatGrid2
- oiw:TableFormatGrid3
- oiw:TableFormatGrid4
- oiw:TableFormatGrid5
- oiw:TableFormatGrid6
- oiw:TableFormatGrid7
- oiw:TableFormatGrid8
- oiw:TableFormatList1
- oiw:TableFormatList2
- oiw:TableFormatList3
- oiw:TableFormatList4
- oiw:TableFormatList5
- oiw:TableFormatList6
- oiw:TableFormatList7
- oiw:TableFormatList8
- oiw:TableFormat3DEffects1
- oiw:TableFormat3DEffects2
- oiw:TableFormat3DEffects3
- oiw:TableFormatProfessional
- oiw:TableFormatSubtle1
- oiw:TableFormatSubtle2
- oiw:TableFormatWeb1
- oiw:TableFormatWeb2
- oiw:TableFormatWeb3
|
Return Values
Returns 1 if successful and zero if it fails. In
case of an error the ErrorTrap method will be called with the error
description.
Example
| Example |
| oiWord.TableAutoFormat(1,
oiw:TableFormatProfessional) |
See Also
TableUpdateAutoFormat
ShowToolbar
ShowToolbar ( long pToolbar ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets a MS Word toolbar to be visible. For a list of valid
equates which can be used, click here.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.ShowToolbar (oiw:ToolbarStandard)
TempByte = MyWord.ShowToolbar (oiw:ToolbarStandard)
|
TableCountColumns
TableCountColumns ( long TableNumber=1 ) ,long
Description
- Returns (long) the number of Columns in a table. If you have
more than one table in a document, you can specify which table with
the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns the number of columns, or a negative value if an error occurred.
Example
| Example |
TempLong = MyWord.TableCountColumns () ! Table 1
TempLong = MyWord.TableCountColumns (3) ! Table 3 |
TableCountRows
TableCountRows ( long TableNumber=1 ) ,long
Description
- Returns (long) the number of Rows in a table. If you have
more than one table in a document, you can specify which table with
the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns the number of rows, or a negative value if an error occurred.
Example
| Example |
TempLong = MyWord.TableCountRows () ! Table 1
TempLong = MyWord.TableCountRows (3) ! Table 3 |
TableGetCellBackgroundColor
TableGetCellBackgroundColor ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber ) ,long
Description
- Returns the background color of a cell within a table.
- If the color value (long) matches any of the standard Clarion color
equates, the method will return that equate (e.g. COLOR:Green), or
it will simply return a long (color).
Example
| Example |
| TempLong = MyWord.TableGetCellBackgroundColor
(1, 3, 4) ! table 1, cell C4 |
TableGetCellForegroundColor
TableGetCellForegroundColor ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber ) ,long
Description
- Returns the foreground color of a cell within a table. If
you have more than one table in a document, you can specify which
table with the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- If the color value (long) matches any of the standard Clarion color
equates, the method will return that equate (e.g. COLOR:Green), or
it will simply return a long (color).
Example
| Example |
| TempLong = MyWord.TableGetCellForegroundColor
(1, 3, 4) ! table 1, cell C4 |
TableGetCellTexture
TableGetCellTexture ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber ) ,long
Description
- Returns the texture of a cell within a table. If you have
more than one table in a document, you can specify which table with
the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- The texture that is returned is a long, which can be one of the
"Texture" equates.
Example
| Example |
| TempLong = MyWord.TableGetCellTexture (1, 3,
4) ! table 1, cell C4 |
TableGetColumnWidth
TableGetColumnWidth ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber ) ,long
Description
- Gets the current width for a table column. If you have more
than one table in a document, you can specify which table with the
TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns the column width (long), or a negative value if an error
occurred.
Example
| Example |
| TempLong = MyWord.TableGetColumnWidth (1, 3)
! table1, column3 |
TableGetInsideBordersLineStyle
TableGetInsideBordersLineStyle ( long TableNumber=1 ) ,byte
Description
- Returns the style of the lines which make up the inside borders
of a table. If you have more than one table in a document, you
can specify which table with the TableNumber parameter, which defaults
to 1.
- See the "LineStyle" Equates for
a list of possible line styles.
Example
| Example |
| TempByte = MyWord.TableGetInsideBordersLineStyle
(3) ! table 3 |
TableGetOutsideBordersLineStyle
TableGetOutsideBordersLineStyle ( long TableNumber=1 ) ,byte
Description
- Returns the style of the lines which make up the outside borders
of a table. If you have more than one table in a document, you
can specify which table with the TableNumber parameter, which defaults
to 1.
- See the "LineStyle" Equates for
a list of possible line styles.
Example
| Example |
| TempByte = MyWord.TableGetOutsideBordersLineStyle
(3) ! table 3 |
TableInsertRowAtEnd
TableInsertRowAtEnd ( long TableNumber=1 ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Inserts a new row after the last current row in a table. If
you have more than one table in a document, you can specify which
table with the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableInsertRowAtEnd () ! table 1
TempByte = MyWord.TableInsertRowAtEnd (3) ! table 3 |
TableMergeSelectedCells
TableMergeSelectedCells ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Merges the currently selected cells in a table (see code example above)
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
! Merge cells B2 and C2
if MyWord.SetSelection (1, 2, 2) ! select cell B2 in table 1
MyWord.MoveRight (oiw:UnitCharacter, 1, oiw:Extend) ! select the cell to
the right also (C2)
MyWord.TableMergeSelectedCells() ! merge the two cells
MyWord.SetSelection (1, 1, 1) ! deselect (select A1)
end |
TableSetCellAlignCenter
TableSetCellAlignCenter ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the alignment within a table's cell to "Centered".
If you have more than one table in a document, you can specify which
table with the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
- TIP - After you call this method
the cell which you set will become active, i.e. that's where your
cursor will be.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetCellAlignCenter (1, 3, 4)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetCellAlignCenter (1, 3, 4) |
TableSetCellAlignJustify
TableSetCellAlignJustify ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the alignment within a table's cell to "Justified".
If you have more than one table in a document, you can specify which
table with the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
- TIP - After you call this method
the cell which you set will become active, i.e. that's where your
cursor will be.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetCellAlignJustify (1, 3, 4)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetCellAlignJustift (1, 3, 4) |
TableSetCellAlignLeft
TableSetCellAlignLeft ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the alignment within a table's cell to "Left Aligned".
If you have more than one table in a document, you can specify which
table with the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
- TIP - After you call this method
the cell which you set will become active, i.e. that's where your
cursor will be.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetCellAlignLeft (1, 3, 4)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetCellAlignLeft (1, 3, 4) |
TableSetCellAlignRight
TableSetCellAlignRight ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the alignment within a table's cell to "Right Aligned".
If you have more than one table in a document, you can specify which
table with the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
- TIP - After you call this method
the cell which you set will become active, i.e. that's where your
cursor will be.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetCellAlignRight (1, 3, 4)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetCellAlignRight (1, 3, 4) |
TableSetCellBackgroundColor
TableSetCellBackgroundColor ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber, long pColor
) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the background color for a cell within a table. If you
have more than one table in a document, you can specify which table
with the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
- The pColor parameter can be a standard Clarion color equate (e.g.
color:red), or a long as returned by one of the oiWord methods, such
as TableGetCellBackgroundColor.
- TIP - The difference between
this method and the TableSetCellForegroundColor method, is as follows:
If you use the TableSetCellTexture method to set a "pattern"
/ "texture" for a cell, then the background color is the
color in the cell "behind" the pattern, whereas the foreground
color is the color of the pattern.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetCellBackgroundColor (1, 3, 4, color:red)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetCellBackgroundColor (1, 3, 4, color:red) |
TableSetCellBold
TableSetCellBold ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber, byte pBold=255
) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the bold formatting within a table's cell. If you have
more than one table in a document, you can specify which table with
the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- The pBold parameter can be one of the following equates:
- oiw:BoldOn
- oiw:BoldOff
- oiw:BoldToggle
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetCellBold (1, 3, 4, oiw:BoldOn)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetCellBold (1, 3, 4, oiw:BoldOn) |
TableSetCellFontColor
TableSetCellFontColor ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber, long FontColor
) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the font color within a table cell. If you have more
than one table in a document, you can specify which table with the
TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetCellFontColor (1, 3, 4, color:Green)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetCellFontColor (1, 3, 4, color:Green) |
TableSetCellFontName
TableSetCellFontName ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber, string FontName
) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the font (name) within a table cell.If you have more
than one table in a document, you can specify which table with the
TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetCellFontName (1, 3, 4, 'Arial')
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetCellFontName (1, 3, 4, 'Arial') |
TableSetCellFontSize
TableSetCellFontSize ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber, long FontSize
) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the font size within a table cell. If you have more than
one table in a document, you can specify which table with the TableNumber
parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetCellFontSize (1, 3, 4, 12)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetCellFontSize (1, 3, 4, 12) |
TableSetCellForegroundColor
TableSetCellForegroundColor ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber, long pColor
) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the foreground color for a cell within a table. If you
have more than one table in a document, you can specify which table
with the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
- The pColor parameter can be a standard Clarion color equate (e.g.
color:red), or a long as returned by one of the oiWord methods, such
as TableGetCellForegroundColor.
- TIP - The difference between
this method and the TableSetCellBackgroundColor method, is as follows:
If you use the TableSetCellTexture method to set a "pattern"
/ "texture" for a cell, then the background color is the
color in the cell "behind" the pattern, whereas the foreground
color is the color of the pattern.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetCellForegroundColor (1, 3, 4, color:red)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetCellForegroundColor (1, 3, 4, color:red) |
TableSetCellItalic
TableSetCellItalic ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber, byte pItalic=255
) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the italic formatting within a table's cell. If you have
more than one table in a document, you can specify which table with
the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- The pItalic parameter can be one of the following equates:
- oiw:ItalicOn
- oiw:ItalicOff
- oiw:BoldItalic
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetCellItalic (1, 3, 4, oiw:ItalicOn)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetCellItalic (1, 3, 4, oiw:ItalicOn) |
TableSetCellTexture
TableSetCellTexture ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber, long pTexture
) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the texture / pattern within a table's cell. If you have
more than one table in a document, you can specify which table with
the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- See the "Texture" Equates
for a list of valid textures (used in the pTexture parameter).
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
- TIP - Use the TableSetCellBackgroundColor
method to change the color "behind" the pattern, and the
TableSetCellForegroundColor method
to change the color of the pattern itself.
- See the reference section titled MS Word
Textures for graphical examples of the available textures.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetCellTexture (1, 3, 4, oiw:TextureCross)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetCellTexture (1, 3, 4, oiw:TextureCross) |
TableSetCellUnderline
TableSetCellUnderline ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber, byte LineStyle=255
) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the underline style / formatting within a table's cell.
If you have more than one table in a document, you can specify which
table with the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- See the "Underline" Equates
for a list of valid line styles (used in the LineStyle parameter).
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetCellUnderline (1, 3, 4, oiw:UnderlineSingle)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetCellUnderline (1, 3, 4, oiw:UnderlineSingle) |
TableSetColumnWidth
TableSetColumnWidth ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long ColumnWidth ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Sets the width for a table column. If you have more than one
table in a document, you can specify which table with the TableNumber
parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetColumnWidth (1, 3, 40)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetColumnWidth (1, 3, 40) |
TableSetInsideBordersLineStyle
TableSetInsideBordersLineStyle ( long TableNumber=1, byte LineStyle ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Changes the style of the lines which make up the inside borders
of a table. If you have more than one table in a document, you
can specify which table with the TableNumber parameter, which defaults
to 1.
- See the "LineStyle" Equates for
a list of possible line styles.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetInsideBordersLineStyle (1, oiw:LineStyleDouble)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetInsideBordersLineStyle (1, oiw:LineStyleDouble) |
TableUpdateAutoFormat
TableUpdateAutoFormat (long tableNumber), long
Description
The
TableAutoFormat
method formats the specified table using one of the styles provided by
Word. These styles apply formatting to both the table and table
contents. When new columns and rows are added the automatic formatting
may not be applied to them, in which case the TableUpdateAutoFormatting
method may be called to apply the same formatting to any new rows and
columns.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| long tableNumber | The number of the table to
format. Word numbers the first table in the document as 1, and each
successive table increments that table number. Note that the tables are
numbered in the order that they occur in, not in the order that they were
added to the table, so if you have two tables and insert a new one between
them the last table is numbered 3, rather than 2. |
Return Values
Returns 1 if successful and zero if it fails. In
case of an error the ErrorTrap method will be called with the error
description.
Example
| Example |
| oiWord.TableUpdateAutoFormat(1) |
See Also
TableAutoFormat
TableSetOutsideBordersLineStyle
TableSetOutsideBordersLineStyle ( long TableNumber=1, byte LineStyle ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Changes the style of the lines which make up the outside borders
of a table. If you have more than one table in a document, you
can specify which table with the TableNumber parameter, which defaults
to 1.
- See the "LineStyle" Equates for
a list of possible line styles.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableSetOutsideBordersLineStyle (1, oiw:LineStyleDouble)
TempByte = MyWord.TableSetOutsideBordersLineStyle (1, oiw:LineStyleDouble) |
TableWriteToCell
TableWriteToCell ( long TableNumber=1, long ColumnNumber, long RowNumber, string pText
) ,byte,proc
Description
- Writes text (string) to a cell within a table. If you have
more than one table in a document, you can specify which table with
the TableNumber parameter, which defaults to 1.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.TableWriteToCell (1, 3, 4, "Cell
C4") ! table 1
TempByte = MyWord.TableWriteToCell (3, 3, 4, "Cell C4") ! table 3 |
TakeEvent
TakeEvent ( string pEventString1, string pEventString2, long pEventNumber=0, byte
pEventType=0, byte pEventStatus=0 )
Description
- Office Inside acts as a bridge between your application and COM
objects. These COM objects communicate with the Office Inside
library, which in turn communicates to COM objects, and to your
application. The library is also constantly communicating with
itself.. Hmm.. Sort of.. Most of this
"background" communication is of little importance to you
the developer, as the Office Inside library will provide you with
any useful information or functionality, through its methods and
properties. Occasionally you may want to "listen" to
this communication "directly", which is what the TakeEvent
method was designed for.
- The TakeEvent method is not a method which you will call
yourselves, but is rather a method that the OI library calls from
several other methods. The only reason this method exists is
to provide a central place where all communication activity is
"reported". This is useful to log the library
activity (as in the Automation examples), or to listen for certain
activity and then deal with it accordingly from your own code.
- The pEventNumber parameter will be one of the values listed
under the Callback Event Equates
(only if pEventType is oi:EventType_Callback).
- The pEventString1
property will contain a string description of whatever event /
method / "thing" triggered the TakeEvent method.
- The pEventType
property is a byte, which will be one of the following values:
- oi:EventType_Callback (indicates the COM object sent a
message to the OI library)
- oi:EventType_MethodCall (indicates a method
in the library has been called)
- oi:EventType_InternalMethodCall (indicates
a method is being called by another method)
- The pEventStatus property only applies if the pEventType
is oiw:EventType_MethodCall, and can be one of the following values:
- oi:EventStatus_Beginning (method has just
been called, and is about to run)
- oi:EventStatus_Complete (method has
completed, and is about to return)
- NOTE: The parameters for this method are "filled in" by
the library for you, and should not be written to / passed back by
you (although if you do change these properties values the library
will just ignore those changes).
TakeSnapShotOfWindowPos
TakeSnapShotOfWindowPos ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- This method updates several internal properties with information
about the current position and state (e.g. maximized) of the MS Word
application window. The templates call this method immediately
after the Init method. It is used in conjunction with the
RestoreSnapShotOfWindowPos method.
Example
| Example |
| MyWord.TakeSnapShotOfWindowPos () |
Underline
Underline ( byte LineStyle ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Make the selected text underlined / not underlined.
- See the "Underline" Equates
for a list of valid line styles (used in the LineStyle parameter).
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.Underline (oiw:UnderlineDouble)
TempByte = MyWord.Underline (oiw:UnderlineNone) |
Undo
Undo ( ) ,byte,proc
Description
- Undoes the last thing you did.
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.Undo()
TempByte = MyWord.Undo() |
Unprotect
Unprotect (string pPassword), long
Description
Removes document protection. Protection limits what changes may be made to the document unless
document protection is turned off. If a password is specified then that
password must be used to turn document protection off. Once you enabled
document protection the same limits that apply to the end user also
apply to other methods called. For example if you enabled document
protection (by calling oiWord.
Protect()) and set
the document to Read Only, you will not be able to
modify the document by calling any of the oiWord methods until oiWord.
Unprotect()
is called to remove the protection.
Parameters
| Parameter |
Description |
| string pPassword | The password that
was used to protect the document. This password will be needed to remove
the protection. A blank string may be specified, if the protection was
added with a blank password. |
Return Values
Returns 1 for success and zero for failure.
Example
| Example |
MyWord1.Unprotect('capesoft')
MyWord1.Unprotect('')
|
Update
Update (byte pOption, string pValue),
long, proc
Description
This is a wrapper method which can update one of several "properties"
or "settings", depending on the parameters which you pass.
- See the GetInfo/Update Equates for
a list of valid values to use in the "pOption" parameter.
- The pValue parameter (string) contains the new value which you want
to update / change.
- If you pass oiw:WindowState as the first parameter, then
the second parameter must be one of the following:
- oiw:RestoreWindow
- oiw:MaximizeWindow
- oiw:MinimizeWindow
- If you pass oiw:PageOrientation as the first parameter,
then the second parameter must be one of the following:
- oiw:OrientLandscape
- oiw:OrientPortrait
- Returns true (1) if no problems were experienced.
Example
| Example |
MyWord.Update (oiw:StatusBar, 'Hello World')
TempByte = MyWord.Update (oiw:WindowState, oiw:MinimizeWindow) |
Before implementing Office Inside's Mail Merge features, we would recommend that
you familiarize yourself with the basics of using MS Word's Mail Merge functionality.
The MS Word help files cover this topic extensively, but here's a starter to get
you going ( although we would recommend spending some time in MS Word learning
about Mail Merging before adding this feature into your apps ).
In a nutshell, Mail Merging consists of reading data from a Data Source ( a file
that contains the information to be merged into the Main Document ); then inserting
data from the data source into the Merge Fields ( placeholders in your main document
) which you have created in your Main Document ( the document that contains the
text / graphics / merge fields ).












 This could also be an xls file (for type
csv).
This could also be an xls file (for type
csv).

