A1.
How many users can this program support?
A2.
Is anti-virus software supported?
A3.
Is spam filtering supported?
A4.
How do I upgrade my Email Server?
A5.
When I upgrade the Email Server will I have to reconfigure it with all my settings?
A6.
How do I backup my configuration settings?
A7.
Understanding SMTP error codes (or "What the
heck does 550 relay denied mean anyway?")
Product Setup & Configuration
B1.
How do I configure my email client (e.g. Outlook / Outlook Express) to read emails from the Email Server?
B2.
My email client (e.g. Outlook / Outlook Express) won't connect to the email server to get or send email. What's going wrong?
B3.
My Server Can't Listen on a Port. What's happening and how do I fix it?
B3.
I am getting "Error. SMTP Server could not listen on the requested port (25)". How do I fix it?
B3.
I am getting "Error. POP3 Server could not listen on the requested port (110)". How do I fix it?
B4.
How do I change the port number that CapeSoft Email Server runs on?
B5.
I don't know any DNS Servers, are there any I can use in the mean time?
B6.
How do I configure Internal Email?
B7.
How do I configure my machine to Auto Logon?
B8.
Some other email servers are rejecting my email because I don't have reverse DNS working. What should I do?
B9.
I
don't seem to be able to send email via the MX method to some domains
(including AOL). Sometimes I see -53, -57, 550, 551, 553, 554, 500 or
451 errors. What's going on?
B10.
How do I block or reject incoming emails for certain email addresses?
B11.
How do I read my mail at home and at work?
B12.
What is the difference between a "Relay Server" and an "Open Relay Server"?
B13.
What are MX entries?
B14.
What is the difference between MX sending and Relay sending?
B15.
What should I set my Sending Relay Server settings to?
B16.
What's the difference between a dynamic IP and a static IP?
B17.
My Dynamic IP address is being blocked by my recipient's server. What can I do?
B18.
How do I implement a Dynamic IP Updater, and which one do you recommend?
B19.
How do I setup my own domain and receive emails for it?
B20.
How do I configure the email server to work on a server with a dynamic IP?
B21.
I'm struggling to send emails from the Email Server to my Relay Server. What can I do?
B22.
I'm struggling to send emails from my Email Client to the Email Server. What can I do?
B23.
Where does Email Server store my mail and settings?
B24.
How do I change where Email Server stores its data (mail and settings)?
B25.
Secure the POP and SMTP server using sTunnel to provide
SSL connections
Running issues, upgrade problems & support related questions
C1)
How do I get help or support for this application?
C2)
How do I generate a LOG file I can email to support?
C3)
What
does this error mean "Could not get write access to .\Data\Emails.tps
so trying read-only" and/or "File .\Data\Emails.tps could not be
opened. Error: Access Denied (5). Press OK to end this application"?
C4)
It looks like the Email Server is saving collected emails to the wrong mailbox. What's going on here?
C5)
I'm running the Email Server as a Service, and I can't find the Icon in the task tray notification area. What's going on?
C6)
How do I delete items from the Outbox or the user mailboxes?
C7)
I'm getting -53 errors - what does this mean?
C8)
When I collect mail my user name or
password is rejected, why can't I connect to the email server?
C9)
I get an API error when writing the SmtpClientLog.xml file
C10)
I upgraded from an older release to 3.80 or 3.81 and had
problems and rolled back. When I install the new release I seem to loose my settings.
C11)
I am running Email Server as a Service under Windows
Vista, but there is no icon in the system tray.
C12)
Why is mail "sticking" in the outbox and not sending?
C13)
After upgrading to Email Server 4.2.0 the email seems
slow and unresponsive (and may be using an excessive amount of CPU time or
memory)
C14)
After upgrading to Email Server it fails to start and displays an "unable to
reload license" error.
Developer Edition
D1)
For all Developer Edition queries please look here
Source Code
E1)
For all Source Code queries please look here
Sending Errors
A1) Question: How many users can this program support?
Answer: CapeSoft Email Server poses no limit on the number of
mailboxes, aliases, or domains you wish to configure. In reality the number of
users the system can support is determined by a number of factors. Things like
speed of the server, speed of the server's hard drive, available memory,
network/Internet bandwidth, amount and size of email traffic, and the efficiency
of the email server all play a part in the equation. At the end of the day there
is no magic number. On a fast machine there should be no problem with several
hundred or more users. Although CapeSoft Email Server not originally
targeted at replacing large (expensive) enterprise level mail servers, over the years it
has increased in speed and efficiency, and we have tested the server on both
fast and even slow (486) machines and it has remained very responsive, and
scales to handle large volumes well.
A2) Question: Is anti-virus software supported?
Answer:
As to be expected, the CapeSoft Email Server in itself contains no virus checking software,
however it does work with
a number of popular Anti-Virus programs, which you will have to
purchase separately. The following information may help you in choosing
which anti-virus software to purchase, as well as some configuration tips.
Anti-Virus software detects viruses in emails via two methods:
- Method 1 : They detect viruses in .eml (email) files that are stored on the disk.
- Method 2 : They detect viruses by acting as a email proxy that intercepts the normal TCP/IP
connections and listens in for viruses.
When you are wanting to install anti-virus software that gives you 100% virus protection to work with this Email
Server,
you'll need an anti-virus program that uses method 1 (i.e. Detect viruses in .eml files).
When the Anti-virus application locks access to the .eml file CapeSoft
Email Server detects this, and the emails containing these viruses are
deleted and not sent to the POP3 recipients or sent out via SMTP.
This means that the sever machine (running CapeSoft Email Server and
the Anti-Virus program) will not receive or pass on known viruses in
emails to any of the machines in your network.
Anti-virus programs that only use Method 2 only protects the email
client transactions (outgoing emails sent via SMTP from the Email
Server, and incoming emails from other Email Servers via
POP Collect to this Email Server), which is only a subset of all the
email server functionality.
So this method does not protect the Email Server
from receiving virus emails via its SMTP Server and
then passing them on to Email Clients via its POP3 Server. The only way
to protect your entire system using this method, would be to ensure
that each computer on the network
is running an anti-virus application that covers method 2, but that's
not a server based solution.
Note:
Another consideration when choosing an anti-virus program is that many
of the standard versions of anti-virus programs do not run on Server
Operating Systems
(for example Windows Server 2003, Windows 2000 Server, Windows NT 4
Server). Anti-virus programs that can run on Server machines are often
more expensive.
(Incidentally there is also no reason from the Email Server software,
why you can't run your Email Server on Desktop Operating Systems like
Windows Vista, Windows XP Pro, Windows XP Home, Windows 2000 Pro, Windows 98 etc.)
Note:
We've added an Anti-Virus Testing Tool to the Email Server, which you
can use to test whether your anti-virus application is working
correctly with method 1,
and therefore protecting your system. This checking tool is available
from the Tools menu in the Email Server.
Note: It's often best to turn off Method 2 from your Anti-Virus software
(sometimes called something like Email Scanning in the Anti-Virus Configuration), for the following reasons:
- Sometimes you can't get your Email Clients to talk to the Email Server, because the Anti-Virus
intercepts the communication but does not know where the Email Server is residing.
- It can make the email transfer slower.
- It can mislead you as an email
may appear to be sent from the Email Server, but all that's happened is
that the Anti-Virus application grabbed the outgoing email,
and the anti-virus application still needs to send it out.
- It can wreak havoc with dial-up accounts.
Here's a list of Anti-Virus software that we have tried out with the Email Server:
- AVG 7 Anti-Virus System (www.grisoft.com) -
Recommended.
Supports method 1.
If you are installing their Anti-Virus software for servers you only
need the File Server version (and not the full Email version of the
virus checker - this can be cheaper).
They also have a free personal version (be sure to read their license
to check if you are eligible)
- Norton Anti Virus (www.symantec.com) - Not recommended.
It does not support method 1 for .eml files.
Their implementation of "Email Scanning" (method 2) will not prevent emails with viruses from entering your system.
- Panda Titanium Antivirus (www.pandasoftware.com) -
Recommended. Supports method 1.
Note:
You must turn on the "scan compressed file" option in Settings - Files
to Scan, otherwise .eml files are not scanned correctly.
- Sophos Anti-Virus (www.sophos.com) - Not recommended.
It does not support method 1 for .eml files.
- Trend Micro Office Suit (www.antivirus.com) -
Recommended.
Supports method 1. (Although you may need to turn on options to look in
zip or archive files so that it does look inside .eml files).
- Trend Micro Internet Security 11 (PC-Cillin) (www.antivirus.com) -
Recommended.
Supports method 1. (But you may need to disable the Email Scanning if
you find you can't get the Email Clients to talk to the Email Server -
but it worked fine here with Email Scanning still on).
A3) Question: Is spam filtering supported?
Answer:
SPAM pesters people on two fronts:
1) Spammers send loads of spam to email addresses in your domain, which
don't actually map to anyone in particular. For example they may send
emails to andrew@example.com even though you don't have an Andrew in
your office. Spammers in fact are actually sending emails to a whole
list of names (e.g. Aaron, Abbi, Abby, Adam, Allan, Allen, Alec, Alex,
Alexa, Alexander, Alexandra, Alexis, Alicia, Allison, Alyssa, Amanda
etc.) in the hope of hitting some real addresses that do exist in your
domain.
This becomes a real problem because although these emails are delivered
to anyone meaningful, they are using your bandwidth, and may be
clogging an email account that you are collecting email from.
Solution:
a) Make sure that any unused email addresses are rejected. See
FAQ B10 on how to block and reject email addresses.
e.g. If you don't have an andrew@example.com at your company, then make sure this email address is being rejected.
b) Turn on the "SPAM Optimization (Download Headers First)" option in
Tools | Options | Collect | Properties for each POP3 account that you are
collecting from. What this does is it tells the Email Server to
download the Email Headers first, and to check that the email is for an
email address that is valid. Rejected emails are then deleted before
they are downloaded. This makes the collecting much quicker and saves
you bandwidth.
2) Spammers also hit real addresses. This is very frustrating as your Email Client's Inbox fills up with loads of junk.
Solution:
a)
The best way to avoid spam is to prevent spam. I have been using the
same email address for the last 6 years, and still only receive minimal
spam messages a day,
whereas some of my colleagues receive literally hundreds of spam emails a day. The
trick is simple:
- Never put your email address on your web site as text or a link, rather display it as a graphic or javascript encrypted link/
(This will prevent spam spiders from reading your email address off your website.)
- Never put your real email address on a news server. Rather do something like this:
andrew@company.nospam.com (any human reader can easily change this back to your real email address)
- Try and avoid easy to guess email addresses like bob@example.com rather use
BobWhite@example.com
(As this is a harder address for spammers to guess.)
b) If spam is really becoming a pain, it may be worth changing your email address from say
bob@example.com to BobWhite@example.com
(but this may not always be practical, but it's very effective). It's
also never too late to start a new domain, where you look after your
email addresses and this can provide your clients with a hotline into
your company that is less entangled with spam.
c) Another very effective way to keep spam at bay, is to use different
email addresses for online activity. What you need to do is setup an
alias of say
BobWhite#@example.com to map to your mailbox, then when you enter your email address at
amazon.com
you can use BobWhiteAmazon@example.com and when you provide your email address for
Joel Spolsky's
news letter you provide BobWhiteJoelOnSoftware@example.com. I always do this, and have found this to be very useful. Then if someone does provide your email address
to other companies) you know where the email address came from and ii) you add a reject alias (see
FAQ B10) to block BobWhiteDodgyCompany@example.com.
This is simply and easy to do.
d) At the moment spam filtering is not built into the CapeSoft Email Server, but there are a number of Spam Filtering packages
that can be used in conjunction with the CapeSoft Email Server.
Some people have been using
POPFile
which is a free product, that implements automatic mail classification
using Bayesian Statistics to categorize your email into spam and
non-spam.
POPFile can be implemented as both a client or a server based system.
(But before you implement this as a server system,
please read the article below).
Here's a very informative article that you should probably read before implementing SPAM filtering:
When are Anti-Spam Techniques not actually helpful - by Bruce Johnson
The biggest problems with Anti-Spam techniques is that legitimate
emails are sometimes thrown away. For this reason it is always better
to
flag emails as spam (e.g. Add the text [Spam]
to the subject line), than to simply delete the emails. This allows the
clients to redirect potential
spam into a spam folder in their email client, which at least allows
them to scan through the folder periodically and find legitimate emails. We see this too often with
ClarionShop emails,
where people order (and pay for) a product, but because their email
server implements a "throw spam away" technique the details of the
email that explains how to license and download the product may never
reach the recipient, who then becomes understandable irate. But all of
this could be resolved if either client side spam filters were implemented
or if server side spam filters marked emails as potential spam, instead
of simply deleting both potential spam and some legitimate emails too.
A4) Question: How do I upgrade my Email Server?
Answer: Upgrades for this product are free. To upgrade this Email Server:
- Download the latest version
- Exit the Email Server
- Run the new install file. This will install the latest version, and it
will keep your current settings.
(Incidentally if you wanted to backup
your configuration settings see FAQ A6 - Backing up your configuration
settings)
Important Note regarding Version
3.80 and later
This release build in Microsoft Vista compatibility and hence the
data is no longer stored in the \CapeSoft Email Server\Data\ directory.
- Email Server now installs to %ProgramFiles%\CapeSoft\Email Server\ which is
C:\Program Files\Capesoft\Email Server\ on
most systems
- Data is stored in the %ProgramData%\CapeSoft\Email Server\.
- Under Windows Vista this: C:\ProgramData\CapeSoft\Email Server\
- Under previous version of Windows this is: C:\Documents and Setting\All Users\Application Data\CapeSoft\Email
Server\
- You must run the Email Server installer on each machine before running
Email Server, if there is a previous version installed then the installer
will upgrade it and move the existing data to the new location.
- When moving Email Server to a different machine run the Email Server
Installer, then simply copy the Data directory over to the new machine. The
entire contents of the Data directory can be moved.
- We will be releasing a backup and migration tool in Email Server that
will allow you to create a single Backup archive of all mail and settings
and load a backup archive to make moving Email Server a two click process
and backing up a "snapshot" of Email Server a single click process.
A5) Question: When I upgrade the Email Server will I have to reconfigure it with all my settings?
Answer: Fortunately not. The upgrades will keep your current Email Server settings.
A6) Question: How do I backup my configuration settings?
Answer: All your configuration settings are found in your
Data folder
(see below for the location of this folder). They are stored in the various .xml files. Simply make copy of these xml files or make a zip archive of them. Email
Server creates a Backup directory in the Data folder
and makes periodic backups of the XML configuration files.
- Data is stored in the %ProgramData%\CapeSoft\Email Server\.
- Under Windows Vista this: C:\ProgramData\CapeSoft\Email Server\
- Under previous version of Windows this is: C:\Documents and Setting\All Users\Application Data\CapeSoft\Email
Server\
- We will be releasing a backup and migration tool in Email Server that
will allow you to create a single Backup archive of all mail and settings
and load a backup archive to make moving Email Server a two click process
and backing up a "snapshot" of Email Server a single click process.
To restore your settings, first exit the Email Server, then restore the xml files and then restart the email server.
A7. Understanding SMTP
error codes (or "What the heck does 550 relay denied mean anyway?")
SMTP error codes are made of three digits:
The first generally tells whether the server accepted the command and if it
could handle it. The five possible values are:
- 1: The server has accepted the command, but does not yet take
action. A confirmation message is required. Currently, this is not used.
- 2: The server has completed the task successfully.
- 3: The server has understood the request, but requires further
information to complete it.
- 4: The server has encountered a temporary failure. If the command
is repeated without any change, it might be completed. Mail servers can use
such temporary failures to keep untrusted senders at bay.
- 5: The server has encountered an error.
The second number gives more information. Its six possible values are:
- 0: A syntax error has occurred.
- 1: Indicates a informational reply, for example to a HELP
request.
- 2: Refers to the connection status.
- 3 and 4 are unspecified.
- 5: Refers to the status of the mail system as a whole and the
mail server in particular.
The last number is even more specific and shows more graduations of the mail
transfer status. This leads us to the detailed list of ESMTP server response
codes, as laid down in RFC 821 and later extensions:
- 211 - A system status message.
- 214 - A help message for a human reader follows.
- 220 - SMTP Service ready.
- 221 - Service closing.
- 250 - Requested action taken and completed. The best message of
them all.
- 251 - The recipient is not local to the server, but the server
will accept and forward the message.
- 252 - The recipient cannot be VRFYed, but the server accepts the
message and attempts delivery.
- 354 - Start message input and end with <CRLF>.<CRLF>. This
indicates that the server is ready to accept the message itself (after you
have told it who it is from and where you want to to go).
- 421 - The service is not available and the connection will be
closed.
- 450 - The requested command failed because the user's mailbox was
unavailable (for example because it was locked). Try again later.
- 451 - The command has been aborted due to a server error. Not
your fault. Maybe let the admin know.
- 452 - The command has been aborted because the server has
insufficient system storage.
The following error messages (500-504) usually generally indicate a conflict
between the two sides of the conversation, generally indicating that one side is
broken, or issuing invalid commands.
- 500 - The server could not recognize the command due to a syntax
error.
- 501 - A syntax error was encountered in command arguments.
- 502 - This command is not implemented.
- 503 - The server has encountered a bad sequence of commands.
- 504 - A command parameter is not implemented.
The 550 range of errors are quite common and essentially indicate that a
requested action was not allowed, often because of an authentication error
(incorrect user name and password etc.). They can also mean that the server
thinks that you are a spammer, or that you are blocklisted.
- 550 - The requested command failed because the user's mailbox was
unavailable (for example because it was not found, or because the command
was rejected for policy reasons).
- 551 - The recipient is not local to the server. The server then
gives a forward address to try.
- 552 - The action was aborted due to exceeded storage allocation.
- 553 - The command was aborted because the mailbox name is
invalid. See FAQ F1 for more information on this error.
- 554 - The transaction failed. The server should provide
additional details, or this was an intermittent error of some sort. Blame
the weather.
B1) Question: How do I setup my email client (e.g. Outlook / Outlook Express) to read emails from the Email Server?
Answer: We've build an
Email Client Wizard
into the Email Server application. It's in the Help menu. Fundamentally
in Outlook or Outlook Express (or whatever Email Client you are using)
you need to tell Outlook that it must now get
it's mail from the CapeSoft Email Server, rather than directly from the
ISP.
a) Load up the Email Client Wizard and
choose the Mailbox (User) you want to setup. Make a note of the various settings it is telling you
about. i.e. the Outgoing and Incoming mail IP numbers (for example
192.168.2.2 - but it may be different on your machine) - also make a note of
the Account Name and Password.
b) Then run:
OutLook Express (I'm using Outlook Express 6.0 here - but it'll be more or
less the same whichever version you use).
- Tools menu
- Accounts option
- Either Add a new Mail account - use the data collected in step (a),
- or highlight an existing Mail account and press the Properties button.
- Go to the Servers tab and set the data collected in step (a)
- Click OK etc.
- Restart Outlook Express and click Send and Receive
OutLook (I'm using Outlook 2002 (part of Office XP) here - but it'll be more or less the same whichever version you use).
- Tools menu
- Email Accounts option
- highlight View or Change Existing Email Accounts
- click Next
- highlight your existing email account in the list. (The list is most likely only 1 entry long).
- click Change
- set the Server Information and Logon Information with the data collected in step (a)
- Click Finish etc.
- Restart Outlook and Send and Receive
B2) Question: My email client (e.g. Outlook / Outlook Express) won't
connect to the email server to get or send email. What's going wrong?
| Email Client | Error Type 1 | Error Type 2 |
| Outlook Express | The connection to the server has failed. Account: 'My Email', Server:
'192.168.2.1', Protocol: POP3, Port: 110, Secure(SSL): No, Socket Error:
10061, Error Number: 0x800CCC0E | Your server has unexpectedly terminated the connection. Possible causes
for this include server problems, network problems, or a long period of
inactivity. Account: 'My Email', Server: '192.168.2.1', Protocol: POP3,
Port: 110, Secure(SSL): No, Socket Error: 10054, Error
Number: 0x800CCC0F |
| Netscape 7 | Could not connect to server <server details>; the connection was refused. | (no error displayed) |
| Opera 7 | POP3 server unavailable. Network problems?[(null)] | (no error displayed) |
Answer: The error occurs because the email client can not
connect to the email server. This can be caused by a number of reasons, and
the following list may help you find the problem:
- Make sure the email server is running. (Seems silly, but it can be
easily overlooked)
- Please make sure you are running the latest version of the Email Server.
There was a small glitch with Outlook in v2.00 of the CapeSoft Email Server,
so it's worth upgrading.
- Look in the "POP3 Server Log" & the "SMTP Server Log" tabs on the main
Email Server window, if you see an entry like the following:
20:46:31 ------------------
20:46:31 Warning. IP Disallowed. Closing new connection from 192.168.2.1
as it fails the IP check.
20:46:31 Warning: Address [192.168.2.1] disallowed.
20:46:31 New connection from 192.168.2.1 to this POP Server received. On
SockID = 4
20:46:10 ------------------
then the IP Filtering is stopping a connection. If the connection that
was barred was a from a legitimate address then you need to adjust the following,
to allow that address to be able to talk with this server:
Look in the Tools-Options in the IP Address Filter tab. It should be setup
to allow connections from the machine you are running the email client on.
If you are getting Error Type 2 in the above table - this
is almost certainly the problem. Here's a screen shot of the default settings.
Remember if your email client is on 198.14.20.20 then you need to add an
entry for this machine.
Note: You can also choose to allow foreign IP addresses to use your SMTP server if you turn on the
Allow SMTP Authentication
option and they specify a correct Username (mailbox name) and Password.
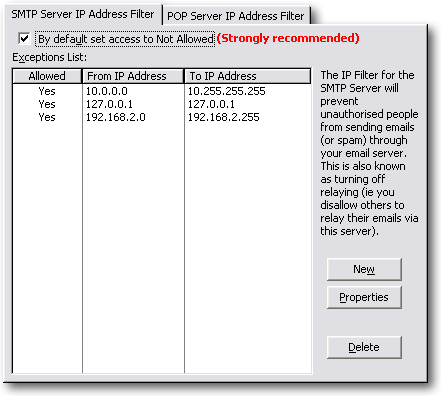
TIP: If you are really unsure
if this is the problem un-tick the "By default allow access to all"
checkboxes for both the SMTP and the POP server. (Remember to add the correct IP Filter entries and re-tick this option later).
- Make sure (in the SMTP Server Log tab and the POP Server Log tab) that
the SMTP Server and POP Server started up correctly. If they have started
correctly then you will see something like:
14:18:18 SMTP Server
listening on port 25
or
14:18:18 POP Server
listening on port 112
If you don't see this or you see some errors about being unable to listen
on the port, then look at the My Server Can't
Listen on a Port FAQ section.
- Are sure the you've entered the correct IP address into the email
account settings in your email client.
- Try running the email client on the same machine as the email server. If
this works but it doesn't work when the email client is on another machine.
Make sure you have the same settings in both email clients. If you do there
may be a problem with the network.
- If while running email client and server on same machine you change (in
the Servers Tab in Outlook Express) the server info to
localhost
instead of something like 192.168.2.1
If this fixes the problem then the IP address you entered into the email
client is incorrect.
- If all else fails, please
generate a log file and send it to
B3) Question: My Server Can't Listen
on a Port. What's happening and how do I fix it? You may see errors like this
in the on-screen logs:
Error. POP Server could not listen on the requested port (110)
Error. SMTP Server could not listen on the requested port (25)
Answer: This error is caused by some other application already using this port.
Typically this will be either an anti-virus application or
another email server application (like IIS's SMTP Service).
Solution 1:Go to
www.sysinternals.com and download
TCPView.
After running this application (and turning on the
Options|Show Unconnected Endpoints option) look to see which application is LISTENING on the local address SMTP port (25) or pop3 port (110).
This is the application that you'll need to close down.
If it's IIS's SMTP Service - you can close this from Computer Manager |
Services and Applications | Internet Information Service.
If it's your Anti-Virus application you should be able to configure this from your Anti-Virus' Control Panel or Options.
Solution 2:If you shutdown the email server and run
netstat -anfrom a command (DOS) prompt you should see an entry like this:
Proto Local Address Foreign Address State
TCP 0.0.0.0:110 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
This means some other program on your machine is listening on port 110.
Do you have other mail programs/virus checkers installed? You can find
the process by elimination. i.e. close down one process at a time
until the listening port disappears.
Solution 3If you are really stumped you can
change the port
on which the CapeSoft Email Server runs but this is not recommended if you are managing a whole domain. As your incoming emails should always be on port 25.
B4) Question: How do I change the port
number that CapeSoft Email Server runs on?
Answer:
Note, please don't change the SMTP port if you are permanently
connected and are running the email server for a whole domain as other email
servers won't know you've changed the port number, and your incoming mail
won't work.
You can do this by going to
Tools | Options | Extra | Advanced,
or if you are still running an older version ...
i) Shut down the CapeSoft Email Server
ii) Open the /program files/capesoft email server/data
folder
iii) Open the options.xml file in a text editor (like notepad)
Tip:
You can double click the XML file which (on most systems) will open the
XML file in Internet Explorer, then choose View-Source from the menu to
open the file in notepad.
iv) Edit the following lines so that they use the port of your choice:
<smtpserverport>25</smtpserverport>
<popserverport>110</popserverport>
v) Change your email client's account settings to use this different port.
B5) Question: I don't know any DNS Servers, are there any I can use in the mean time?
Answer: Your
ISP
are the best people to ask if you are trying to find out what DNS
Server you should be using, but in the mean time you could use
one of the following (remember just to use just the numbers - and not the text description):
- 216.231.128.2 (ezy.net)
- 216.231.128.3 (ezy.net)
- 207.69.188.185 (mindspring.com (earthlink.net))
- 207.69.188.186
- 207.69.188.187
- 168.95.1.1 (dns.hinet.net - taiwan?)
- 196.2.16.3 (mweb - south africa)
- 196.25.1.9 (saix - south africa - cape town)
- 196.43.1.14 (saix - south africa - johannesburg)
B6) Question: How do I configure Internal Email?
Answer: The mail server configuration is described in the
Configuration Section, but the following may also be helpful.
You can setup internal email via three ways:
- 1) If you have a domain (e.g. abcproduct.com) then add abcproduct.com to
the Domains list (Tools-Options), add a mailbox. For example: fred
Then if you send a message to fred@abcproduct.com it will end up in the
fred's mailbox
(You can add extra aliases to point to fred as well. e.g. sales@abcproduct.com)
- 2) If you don't have a domain, you can create a fake one. For example:
ouroffice.com (add this to this domains list in Tools-Options).
Create a fred mailbox and then send an email to fred@ouroffice.com and it will get
into his mailbox.
- 3) Or, simply create a fred mailbox.
Add an alias fred@ouroffice.com (mapped to fred) and then fred will receive
mail for fred@ourOffice.com
(In points 2 and 3 you could also use
ourOffice instead of
ourOffice.com or in fact any domain of your choice, but try and avoid using domains that do exist (e.g. microsoft.com))
B7) Question: How do I configure my machine to Auto Logon?
Answer:
There are two ways to do this. You can either make changes to your
registry, or you can download the Microsoft TweakUI program for your
operating system.
This application has an option to turn on AutoLogon, which means that
you don't have to select a user and enter a password, this is done
automatically when you computer boots up.
Windows Server 2003 & Windows XP:
www.microsoft.com/windowsxp/pro/downloads/powertoys.asp
Windows 2000, Windows NT, Windows ME, Windows 98 & 95:
www.microsoft.com/ntworkstation/downloads/PowerToys/Networking/NTTweakUI.asp
Note: In v3.00 and later you can install your Email Server as a Service. Use the Service commands in the Tools menu to do this.
B8) Question: Some other email servers are rejecting my email because I don't have reverse DNS working. What should I do??
Answer:
Unfortunately some email severs are configured to bounce back email
that comes from another server that does not have a valid reverse
DNS entry. This tragically, is a lame method for trying to stop spam, and usually
results in allowing spam and blocking legitimate emails.
(See this article on
anti-spam techniques that are not useful).
What you can do:
- Ignore it and hopefully sooner (or later) people will work out that
reverse DNS is an invalid technique to stop spam. [Since writing this FAQ (a
couple of years ago) Reverse DNS has become less and less popular and so you
probably won't be too bothered by this]
- Or, set up reverse DNS for your email server. This normally needs to be
done via your ISP, unless you have your own class C network (i.e. All 256 IP
addresses, in which case you can do this yourself).
B9) Question:
I don't seem to be able to send email via the MX method to some domains
(including AOL). Sometimes I see -53, -57, 550, 551, 553, 554, 500 or
451 errors. What's going on?
Answer:
If you are able to send email to most people, but not to a few
addresses (AOL and American Express being the largest culprits
- but there are others), then what's probably happening here is that
your ISP has blacklisted it's dynamic IP addresses on a public IP
blacklist.
Some companies (AOL included) in a desperate (yet
insane)
attempt to reduce spam use these lists to prevent folk on dynamic IP machines
from sending emails directly. Understandably this will prevent a
large amount of spam, but the
baby is thrown out with the bath water and many legitimate emails are
also blocked. This is a really feeble method to try
and prevent spam,
as spammers are well aware of this and will work around it,
meanwhile legitimate email is unable to reach the recipients.
(See this article on
anti-spam techniques that are not useful).
Fortunately we've implemented a work around so that you can specify
that emails that are blocked in this manner are sent through your relay
server settings.
Your email delivery is then in the hands of your ISP, but there's still
a chance that your email can be delivered by your ISP (as long as your
ISP hasn't ended up on someone's spam-was-sent-by-there-IP-addresses
list)..
What you can do:
Go to Tools | Options | Sending Tab and turn on the two "If MX Fails pass email onto Relay Server" options.
Important: See also the FAQ articles
B14 to
B17.
SMTP Reply Codes
211 system status, or system help reply
214 help message
220 <domain> service ready
221 <domain> service closing transmission channel
250 request mail action okay, completed
251 user not local, will forward to <forward-path>
354 start mail input; and with <CRLF>.<CRLF>
421 <domain> servers not available, closing transmission channel
450 requested mail action not taken: mailbox unavailable
451 requested action aborted: local error in processing
452 requested action not taken: insufficient system storage
500 syntax error, command unrecognized
501 syntax error in parameters or arguments
502 command not implemented
503 bad sequence of commands
504 command parameter not implemented
550 requested action not taken: mailbox unavailable
551 user not local; please try <forward-path>
552 requested mail action aborted: exceeded storage allocation
553 requested action not taken: mailbox name not allowed
554 transaction failed
B10) Question: How do I block or reject incoming emails for certain email addresses?
Answer: This can be a really useful thing to do. For example if one of your staff leaves your company, or
you have an email address that is being spammed, but it is never used for legitimate emails (e.g.
paul@yourcompany.com).

In Tools-Options you can set one of two rejection options on a mailbox. You can choose to either simply reject the email or
you can allow emails to be downloaded and be thrown away in the background.
If you are managing your own domain(s) and this email server is
configured to be the incoming SMTP Server, then choosing the first
option will reject any emails before they are sent
to your server.
Tip
You may also want to reject all emails that do not match a valid email alias.
Warning. Make sure you get your alias list set up correctly before using this option.
Here's how to do this:
Create a mailbox called
Reject or
Dumpster and set the reject option on.
Then add an alias of
*@yourcompany.com and map this to the
Reject mailbox.
(The * at the front of the alias means match all combinations of the
alias, that are not specifically defined in the alias list. e.g.
if you have a mailbox for
john@yourcompany.com, then john will still continue to receive his email.)
Note:
On
your network you are able to send an email to multiple people in one
go. Make sure none of these recipients are in the rejected state,
otherwise your email will get stuck in your outbox.
B11) Question: How can I get my mail at work and at home?
Situation One: You want all emails at home and at work
Let's first look at the question in a little more detail. Here's the typical
question:
I have a client that has two computers in her office networked
together.
One is her main computer and she usually reads her email from that
computer.
At night she uses her home computer [or maybe a laptop] to do work and
occasionally needs to refer to an email that she has already seen at
work.
Currently she has no way to do this and I thought your email server
might be a good solution for her.
Can the email server hold all messages as a giant storage facility?
If you're at computer A and you do a send/receive will the email server give you all messages not seen by that machine and
then if you do the same thing on the other machine get all messages not seen by THAT machine.
The idea is suppose there are three new messages grabbed by the email server. When Computer A does a send/receive it
would get the three messages and when at a later time Computer B does a send/receive it will get those same three messages
plus any other new ones. Finally, the next day when Computer A again does a send/receive it should get any new messages
after those original three.
Answer: Take for example
jane@example.comCreate two mailboxes
jane@example.com and jane2@example.com
Then create an alias for
jane@examples.com to mailbox
jane2@example.com
That way when an email comes in for
jane@example.com it will get put into both mailboxes.
Configure computer A to read emails from mailbox
jane@example.com and computer B from
jane2@example.comAside: If you wanted to map say
info@example.com to both mailboxes too, then add two aliases:
info@example.com to
jane@example.com and
info@example.com to
jane2@example.com
Situation Two:
You want all emails at work, but you also want to be able to
read emails - that arrive after you leave work - at home in
the evenings.
This is fairly easy to do.
- At work configure your email client to read and delete emails (the
normal behaviour of most email clients - like Outlook and Outlook Express)
- At home configure your email client to read emails from the same
mailbox, but not to delete the emails until they are 30 days old.
- Then configure the Email Server's IP address Filter so that you can
access the Email Server from your home IP address.
B12) Question: What is the difference between a "Relay Server" and an "Open Relay Server"?
Answer: To answer this question it's probably worth looking at a couple definitions:
A "Relay Server" simply means an email server that you are able to pass
an email onto. Your ISP's email server is a relay server. You can send
it emails, and it will deliver them.
An "Open Relay Server" means a Relay Server that is open to anyone.
This is a bad thing, as it allows anyone to use the email server, which
costs someone bandwidth and is often used for sending spam.
The CapeSoft Email Server allows you to configure itself (using IP
filters) so that it is
not an Open Relay Server. The default settings
prevent it from being an open relay server.
Incidentally, these IP filters allow you to allow "friendly" IP
addresses to send emails through your server should you wish to.
Alternatively the CapeSoft Email Server supports SMTP Authentication,
which means that for someone (outside of your safe IP list) to send
email through the server they must supply a correct username and
password. This option is particularly useful when you have folk who
travel away from your office, but still want to be able to send emails
via say a laptop.
You can test your email server to see if it is operating as an open relay from this site:
www.abuse.net/relay.html
B13) Question: What are MX entries?
Answer: Maybe we should first step back and explain DNS. DNS stands for Domain Name Server, and it is used to map
Domain Names with IP addresses. For example
www.google.com maps to IP address
207.196.25.11. (In fact this is actually a DNS A record.)
DNS MX records do a similar thing, they map the Domain to the responsible
Mail Servers. So for example the MX records for google.com are:
smtp1.google.com - preference 10
smtp2.google.com - preference 10
smtp5.google.com - preference 10
smtp3.google.com - preference 40
smtp4.google.com - preference 40
This means that emails to anybody@google.com will be mapped to one of those mail servers.
Incidentally to list these MX records you can use either of two approaches:
- You can examine the MX entries of a domain by using one of the following
online DNS tools:
here (Type in Domain (e.g example.com) and set Query Type to MX),
here (Type in Domain (e.g. example.com) and set Query Type to MX) or
here (Type in Domain (e.g. example.com) and set Query Type to MX - Mail Exchange Server).
(Remember it can take up to 2 days to get updated around the Internet).
- in a DOS prompt type (you must be online too):
nslookup
set type=mx
google.com
[Ctrl-C] (to break)
MX Entries have two implications when configuring a Mail Server:
- If you administer your own domain, then you will need to configure the
MX records for your domain to point to your Email Server, so that other
people can send your email.
- In the Email Server's Sending configuration you can choose whether to
send email to another Relay Server or rather to send it directly (via
MX). The difference between these two approaches is discussed in
FAQ Article B14.
Here's an example DNS setup for example.com
A Records:
www.example.com - to be pointed to the web server IP address
mail.example.com - to be pointed to the mail server IP address
MX Records:
mail.example.com preference 5
B14) Question: What is the difference between MX sending and Relay sending?
Answer: Email Servers can send emails via two methods:
- Relay Sending - this
approach is where your Email Server passes on the emails to another
Email Server, who is then responsible for delivering the emails. This
approach is like one post office passing on all their letters for
delivery to another post office.
This approach is normally used for dial-up connections as it's a bit
faster, but provides you with less control and slower (or no) feedback
of failed messages.
- This approach uses the recipient's domain MX entries to deliver the
email directly to the recipients email server.
(See FAQ B13 - What is an MX Entry). For
example if you were to send an email to anybody@google.com this
approach would result in the email being delivered directly to one of
the Google email servers.
This approach is the preferred
choice for permanent connections, as it provides you with more control
and better feedback in terms of failed messages.
See also FAQ Article B9 and
FAQ Article B17 on using MX Sending and Relay Sending together.
B15) Question: What should I set my Relay Server settings in the Email Server's Sending Configuration Settings to?
Answer: Your Relay Server (in Tools | Options | Sending Tab | Relay Server) should be set to the Relay Server that your
ISP
provides you with. This will be different for each ISP, although it
will typically be something like mail.yourISP.com or smtp.yourISP.com.
If you are unsure, please look on your ISP's website, as it's often
available there, or give them a ring.
B16) Question: What's the difference between a dynamic IP and a static IP?
Answer:
A static IP is an IP address that is assigned to your server (or
router) that does not change from day-to-day and week-to-week, in fact
it typically does not change from year-to-year. A dynamic IP address is
however an IP address that typically changes reasonably often (typically everyday) to a new address.
ISPs may implement dynamic IP
allocation to broadband (ADSL / DSL / Cable) routers/servers. I
suppose they do this to discourage people from running server
applications, but in reality people still do, it just takes a little
program called a Dynamic IP updater to keep your
DNS Entries up-to-date with your ever changing IP address.
See also:
FAQ Article B17 - My Dynamic IP address is being blocked by my recipient's server. What can I do?
FAQ Article B18 - How do I implement a Dynamic IP Updater, and which one do you recommend?
B17) Question: My Dynamic IP address is being blocked by my recipient's server. What can I do?
Answer:
Using both MX and Relaying
Modern day spam filtering has really made it hard for the users of dynamic IP addresses.
Many prominent companies have deployed spam filtering techniques that
prevent email servers running on dynamic IP addresses from sending
emails to their servers. As a result a large quantity of legitimate
email is barred or lost in the process. This Email Server allows you to
use MX sending by default, but when it encounters a domain that refuses
email from a dynamic IP it will switch to sending that email via your
Relay Server. You can enable this option in Tools | Options | Sending
Tab | MX Settings Tab | If MX Fails pass email onto Relay Server
(Intelligently or Always).
See also
FAQ Article B9.
B18) Question: How do I implement a Dynamic IP Updater, and which one do you recommend?
Solution One:
For a typical domain you'll want to set up the following
DNS Entries:
A Records:
www.example.com - to be pointed to the web server IP address
mail.example.com - to be pointed to the mail server IP address
MX Records:
mail.example.com preference 5
Presuming that you are running your web server and mail server on a server that has a
Dynamic IP address you would need to configure a dynamic IP updater to update the following entries:
www.example.com
mail.example.com
I would recommend DirectUpdate (
www.directupdate.net
price: $15 or $20) which allows you to update your DNS Server entries
stored at www.zoneedit.com (which allows you to administer 5 domains
for free).
Solution Two:
Another approach is to mix in two Dynamic IP updaters. This gives you the
benefit of having a backup system. Here's how you would need to
configure your
DNS Entries:
A Records:
www.example.com - to be pointed to the web server IP address
mail.example.com - to be pointed to the mail server IP address
MX Records:
mail.example.com preference 5
examplecompany.no-ip.com preference 10
You would then need to configure the following entries in DirectUpdate
www.example.com
mail.example.com
And then configure a No-IP entry for examplecompany.no-ip.com. (
www.no-ip.com -
have a free dynamic service and a small application that you need to run).
B19) Question: How do I setup my own domain and receive emails for it?
Answer: You'll need to do the following:
- You'll need to register yourself a domain. You have to do this using a
Domain Registrar. I've used a number of them, but have been very happy with
www.aplus.net. This will typically cost somewhere around $6 to $30 a year, depending on which company you use.
- If you are going to be hosting your email server on a dynamic IP
address (as is often the case with Broadband ADSL / DSL connections),
then you'll need to setup a dynamic IP updater. This is fairly easy to
do, see FAQ B18.
- Once your domain has been registered (can take a day or two), you'll need to configure your
Domain's Name Servers so that you can configure your own DNS entries
for your domain. You could get your ISP to do this, but it's probably
easier to use www.zoneedit.com. You'll need to create yourself a new zone here, and configure the following (assuming your domain is example.com):
Just follow the following example, choosing the correct options (in italics)
IP Addresses:
example.com (IP Address of where your web page will be hosted)
www.example.com (IP Address of where your web page will be hosted)
(1) For your Email Server's static IP address:
mail.example.com (IP Address of where your Email Server is running.
Make sure this is not a 192.168.x.x or 127.0.0.1 or 169.254.x.x)
(2) For your Email Server's dynamic IP address where you just use no-ip.com dynamic updater:
yourdomain.no-ip.com (IP Address of
where your Email Server is running. You'll need to be using the
no-ip.com program to keep this up-to-date)
(3) For your Email Server's
dynamic IP address where you use both no-ip.com and mail.example.com as
a dynamic updated entry on zoneedit:
yourdomain.no-ip.com (IP Address of where your Email Server is running.
You'll need to be using the no-ip.com program to keep this up-to-date)
mail.example.com (IP Address of where
your Email Server is running. You'll need to be using a program like
xxx to keep this up-to-date at zoneedit)
Mail Servers (MX):
(1) For your Email Server's static IP address:
mail.example.com handling mail 1st
(2) For your Email Server's dynamic IP address where you just use no-ip.com dynamic updater:
yourdomain.no-ip.com handling mail 1st
(3) For your Email Server's dynamic IP address where you use both
no-ip.com and mail.example.com as a dynamic updated entry on zoneedit:
yourdomain.no-ip.com handling mail 1st
mail.example.com handling mail 2nd
Mail Forwards:
Make sure these are off. You don't want these on.
Alternate options:
TIP : You can have multiple MX addresses for your email. In
other words you might want to set it so that _your_ machine is the
"primary mail server" - but your ISP is the "secondary (or tertiary)
mail server" - that way if your server goes offline your mail still
goes to your ISP and doesn't get lost. (You would then collect email
from your ISP's mailbox too).
- Now you'll need to enter the Nameservers that zoneedit provides you
with into your Domain configuration (setup at your Domain Registrar).
This can take up to 2 days to propagate around the Internet, so please be patient.
- Now you just need to make sure you have your Email Server running on
that machine and you will start receiving emails for that domain.
-
You can check your settings by typing in your domain (and doing an
MX lookup online):
here (Type in Domain (e.g example.com) and set Query Type to MX),
here (Type in Domain (e.g. example.com) and set Query Type to MX) or
here (Type in Domain (e.g. example.com) and set Query Type to MX - Mail Exchange Server).
(Remember it can take up to 2 days to get updated around the Internet).
If your domain is setup correctly you should see something like this:
Server: tethys.ringofsaturn.com
Address: 64.81.112.182#53
Non-authoritative answer:
beachpalm.com mail exchanger = 0 mail.beachpalm.com.
Authoritative answers can be found from:
beachpalm.com nameserver = ns14.zoneedit.com.
beachpalm.com nameserver = ns19.zoneedit.com.
mail.beachpalm.com internet address = 203.146.145.194
ns14.zoneedit.com internet address = 209.126.137.108
ns19.zoneedit.com internet address = 69.10.134.196
-
Another TIP
: Ironically about the only machines that can't get to your server via
the No-IP address are machines on your LAN. This is because you are
"inside" your router - everyone outside the router can see your router,
but you can't. This makes testing a lot of fun because you can't just
send yourself an email to see if it works :)
In this case try sending from a web email system - like
hotmail.
B20) Question: How do I configure the Email Server to work on a server with a dynamic IP?
Answer: This is all explained in
FAQ Article B18.
B21) Question: I'm struggling to send emails from the Email Server to my Relay Server. What can I do?
Answer:
- Please check which version of the Email Server are you using? It's
always worth running the latest version when trying to diagnose problems, as
your problem may well have been fixed in the latest version.
- Do you have a valid HELO field in Tools | Options in the Send Tab? The
best thing is to leave this blank.
- Make sure you don't have a RelayServer Login and Password (in Tools | Options | Sending Tab), unless your server requires it.
- Failing all else, please generate a LOG file and send it to us.
B22) Question: I'm struggling to send emails from my Email Client to the Email Server. What can I do?
Answer:
- Please check which version of the Email Server are you using? It's
always worth running the latest version when trying to diagnose problems, as
your problem may well have been fixed in the latest version.
- Is your Email Server is not running on one of the following IP
addresses, then you'll need to add the relevant IP address range to the IP
Filter in Tools|Options:
192.168.x.x
10.x.x.x
169.x.x.x <- this
indicates you are trying to use DHCP, but your DHCP server is not
running
- Please make sure the machine running the CapeSoft Email Server, has this
application unblocked in your firewall (or Windows Firewall) software. Try
disabling your Windows Firewall and any other Firewall you have. Then
restart the Email Server, if this fixes the problem, then you have
identified it. Don't forget to start your Firewall again, after you have
added the Email Server to its exclude/allow list.
- Did you see anything on the SMTP Server Log on the main screen of the
email server This will sometimes tell you what's wrong.
- Double check you have used the correct IP address / hostname settings so
that your Email Client knows which Email Server to send the email to. You
can use the Help | Wizards | Email Client Setup wizard to do this. Use the
IP address of your server and not a hostname, as if there is a DNS problem,
your hostname will not be available.
- Some AntiVirus applications interfere with Email Servers by
running Email Checking Proxies on the same port numbers than Email
Servers use. So it may be worth temporality disabling any
Anti-Virus software.
- Failing all else, please generate a LOG file and send it to us.
B23) Question: Where does Email Server store my mail and
settings?
In versions prior to 3.80 Email Server stored all mail and settings in the
Email Server program directory in a subdirectory called Data. In Email Server
3.80 and above the data is stored in the standard application data location
according to the Microsoft Windows specifications to ensure compatibility with
Windows Vista and new versions of Windows. From version 3.80 onwards the data is stored in
%ProgramData%\CapeSoft\Email Server\.
- Under Windows Vista this usually:
C:\ProgramData\CapeSoft\Email Server\
- Under previous version of Windows this is usually:
C:\Documents and Setting\All
Users\Application Data\CapeSoft\Email Server\
B24) Question: How do I change where
Email Server stores my mail and settings (Advanced)?
We recommend that you do not change the standard locations unless you have
to, and that you only do so if you are comfortable moving files and changing
registry keys.
- Shut down CapeSoft Email Server.
- Run RegEdit (Press the Windows Key + R, type "regedit" and press enter)
- Go to the key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\CapeSoft\Email Server\
- Edit the DataPath value and change the
contents to the full path of directory that you wish to store the data in.
- Close RegEdit.
- Move the data from the default directory (see Question B23) to the new
location that you specified.
- Restart Email Server
B25
Securing the POP and SMTP server using sTunnel (Advanced)
This allows you to use secure connections for mail clients
(and other server) connecting to Email Server to send and receive mail.
Your can download the binaries from:
http://www.stunnel.org/download/binaries.html
You will need an SSL certificate on the server establish a secure SSL
connection. You then need to edit the stunnel.conf configuration file so that
sTunnel knows who ports to listen on, so the stunnel.conf file looks like this:
cert = stunnel.pem
key = stunnel.pem
# Service POP
[stunnel.pop]
accept = <ip-address of server>:465
connect = 127.0.0.1:110
protocol = smtp
# Service SMTP
[stunnel.smtp]
accept = <ip-address of server>:995
connect = 127.0.0.1:25
protocol = smtp
Now when you run sTunnel it will listen on ports 465 and 995 on the IP address
that you specify and redirect any traffic to the local SMTP and POP servers,
allowing for a secure external connection. The connect= statements in the
example above actually don't need an IP address, if you just use the port then
it assume that the connection is to the localhost. The IP addresses above are
simply for clarity.
See http://www.stunnel.org/faq/stunnel.html#configuration_file for a full
description of all available options.
C1) Question: How do I get help or support for this application?
Answer: There's a section in this document all about
getting support and help.
C2) Question: How do I generate a LOG file I can email to support?
Answer:
- If you download
the Debug build of the CapeSoft Email Server it contains more logging
information (but it's also a slightly larger download and will run
slightly slower).
- Please download SysInternal's DebugView (from
www.microsoft.com)
it's a small (170K) download
DebugView:
Information
DebugView:
Download
- Shutdown your CapeSoft Email Server
- Run DebugView
- Click on the Windows Start button, then Programs, then
CapeSoft Email Server,
then Special Debug Version
This will log all the behind the scenes communication to the DebugView application.
- Once your problem has been logged to DebugView, then in DebugView in the
File menu choose the Save
option. Save the file, then zip it and then email it to
 .
Please also note the standard version of the Email Server will also
generate a summary log to DebugView. This can be toggled on and off in the
Tools-Options Advanced tab.
.
Please also note the standard version of the Email Server will also
generate a summary log to DebugView. This can be toggled on and off in the
Tools-Options Advanced tab.
C3) What does this error mean:
"Could not get write access to .\Data\Emails.tps so trying read-only" and/or
"File .\Data\Emails.tps could not be opened. Error: Access Denied (5). Press OK to end this application"?
Answer: This means two things:
1) You are using an older version of the CapeSoft Email Server, and
2) You are running the application twice.
When you run the application it runs as a small white email icon next
to the clock (in the Notification area). Just click on this icon to
open the application.
If you still can't see the icon but are getting the error messages,
then press Ctrl-Alt-Del and End Task the EmailServer.exe application
and start it again from the Start menu.
(It's probably also worth making sure you are running the latest version from
www.capesoft.com)
C4) It looks like the Email Server is saving collected emails to the wrong mailbox. What's going on here?
Answer: Emails have a real recipient address, which may not be listed in the To or CC field.
For example it's possible to send an email to fred@example.com while setting the To field in the Email to bob@example.com.
You can check this by looking in the Email Full Header, and you'll see
something like the following, where this email was actually sent to
fred@example.com:
Return-Path: <bruce@example.com>
Received: from hobbes ([192.168.2.2])
by earth [192.168.2.10]
(running Email Server v2.20 build 85)
with SMTP id <sender:bruce@example.com>
for <fred@example.com>; Wed, 9 Feb 2006 09:38:33 +0200
From: "Bruce" <bruce@example.com>
To: "Bob" <bob@example.com>
...
From v2.20 onwards, this real recipient is listed in the Email Server logs:
11:12:31 Collected email 12 of 20 (3KB) for [fred@example.com] from ["Bruce" <bruce@example.com>] to ["Bob" <example.com>]
C5) I'm running the Email Server as a Service, and I can't find the Icon in the task tray notification area. What's going on?
Answer:
When you run the CapeSoft Email Server as a service, only one person
who is logged into the computer can see the task-tray icon at a time.
This is a result of the Service binding itself to the Desktop
of the first person who logs in.
Also, if you use Remote Desktop to
access your server, you will not be able to see the task bar icon. This is
because a service can't interact with a remote desktop's session.
To display the CapeSoft Email Server window you can do either of the following:
1) Logout your session, and log in to the session (user) that has the Email Server bound to it, or
2) Kill the service (either via Task Manager or via the Windows Service
Manager (type services.msc in the Start | Run window)), and then
restart the application in EXE mode (by choosing the CapeSoft
Email Server icon from the Start | Programs Menu.
We may implement a Web Admin interface that may make this process easier too.
C6) How do I delete items from the Outbox or the user mailboxes?
Answer:
You can view, edit or delete emails for the Outbox and all the other
user Mailboxes, by choosing the Tools | View or Edit the Outbox (or
MailBox) Emails.
This opens up the Windows folder in which the .eml files are stored. To
view items simply double click on them, and they will open up in your
Email Client (typically Outlook Express).
To delete emails:
- Identify which email it is that you want to delete.
- Delete the email off the disk
- Choose the Tools | Advanced | ReRead EML files (when next idle)
When the Email Server next has no active incoming or outgoing connections, it will re-read the EML files off the disk.
C7) I'm getting -53 errors - what does this mean?
Answer: -53 errors occur because a connection could not be established to the
remote server and port. It's very easy to test:
Supposing you were getting -53 errors to smtp.example.com on port 25, then type the following in DOS:
telnet smtp.example.com 25
If this succeeds you should see something like this:
220 SMTP Server Ready
If you don't see something like this, then one of two things is the case:
- Firstly this could indicate that the remote server and port are not
actually there., or
- Something has gone wrong with your network configuration, network
hardware, DNS server, routers, ISP, firewall, internet security,
dial-up/ADSL etc., or possibly even your anti-virus program (e.g. Try
turning off Norton) and this results in your computer being unable to
connect to this remote server and port. In this case, you will need your
network administrator to fix the situation, so that you can connect to this
remote machine.
See also
FAQ B9.
C8)When I
collect mail my user name or password is rejected, why can't I connect to the
email server?
This is actually not an uncommon issue.
There are only two reasons that this occurs:
1) The user name or password is
incorrect. Make sure that if the username is not the entire email address
you only specify the user name in the mail client. The name and password are
case sensitive.
2) The server that you are connecting to
is not the CapeSoft Email Server. This is actually the most common cause of
this problem. To verify this open a command prompt:
- Click on the Start menu, choose Run
and type "cmd" and press enter.
- Type the following in the command
prompt window that opens:
Telnet 127.0.0.1 110
- Press enter and the email server will
display:
+OK CapeSoft Email Server v3.50 Beta build 114
www.capesoft.com POP Server Ready
[353]
If you do not get the CapeSoft Email Server displaying a welcome message
then there is another application running on port 110.
The Telnet command lets you connect to an
IP address and a port and is a great tool for checking the connection to an
email server. From any machine on the LAN (or anywhere else) you can type
"Telnet 192.168.x.x 110" where 192.168.x.x is the IP address, and 110 is the
port that Email Server is running on. If the machine can connect to Email
Server you will get the CapeSoft Email Server welcome message. If you get no
response, or a response that is not like the one above then you cannot
connect, or there is a different application running on port 110. This may
be another email server, or an anti virus/firewall solution that runs as a
proxy.
C9) I get an API error when
writing the SmtpClientLog.xml file, which displays a message and stops the
Email Server from working.
Please upgrade to Email Server 3.83, which resolves this issue. This only
occurred in Email Server 3.80 to 3.82.
C10) I upgraded from an older
release to 3.80 or 3.81 and had problems and rolled back. When I install the
new release I seem to loose my settings.
-
Upgrading: If you have run version 3.80
or later and upgraded a previous release of Email Server it would have
created the new application data directory (see below for the location).
If this directory exists then it is used and no data is moved. If you have rolled back to a previous
release, or you are using a previous release and would like to upgrade
it the you must delete the directory :%ProgramData%\CapeSoft\Email Server\
if it exists.
- Under Windows Vista this:
C:\ProgramData\CapeSoft\Email Server\
- Under previous version of Windows this is:
C:\Documents and Setting\All
Users\Application Data\CapeSoft\Email Server\
- If you do not delete this folder then the installer will not run an
"upgrade" install, and will simply use the data that is already in that
directory, which may result in the settings appears to have been lost.
In this case you can also manually copy the data from the old \CapeSoft
Email Server\Data\ directory to the new data storage directory after the
new version is installed.
C11) I am running Email
Server as a Service under Windows Vista, but there is no icon in the system
tray.
Under Windows Vista services may not interact with the
Desktop. This means that when run as a service, Email Server cannot display
a user interface. To configure Email Server under Vista stop the service,
run Email Server normally, configure it, and then either choose the Install
and Start service option from the Tool->Services menu, or close Email Server
and manually start the service.
C12) Why is email "sticking" in the outbox and not
sending?
One of the more common technical queries for Email Server relates to
mail failing to send, or the outbox "locking up" and not seeming to send
mail. In these cases the logs allow you to diagnose the reason that
Email Server is failing to send mail, usually it is a combination of various intermittent network problems:
- Problem: The log shows that DNS request failing on invalid
domains. DNS servers are retried, which will slow down mail sending.
- Solution: Reduce the number of DNS server and
use DNS Servers that are reliable.
- Tip: When one or more of the DNS server are
down, legitimate mail will typically still be sent as some DNS lookups continued to work
(although some of the servers may return invalid data or timed out, slowing the
server down). Mail with invalid addresses will fail the MX lookup, and and retried periodically for 48
hours, and then returned to the sender (which is often the reason that people
see mail "sticking" in the outbox).
- Problem: A significant amount of mail fails to send
is that the server it is sent rejects it, primarily with 550 (relay
denied) errors.
- Reason: Your server may be on a blocklist,
which you should endeavor to resolve with the specific blocklisting
service, or your server may not have a legitimate reverse DNS, or a
SPF Record. Your Relay server login may have changed and you are
using an invalid login; or you are providing SMTP Auth details when
not required; or you are not providing SMTP Auth details when they
are required; or your SMTP relay server may have moved to using a
different port or an SSL connection (in which case you will get
connection failure errors).
- Problem: Your DNS servers were experiencing timeouts, which causes
delays in mail sending; or at least one of the DNS server returns
invalidly formatted DNS packets (you will see a "J_Position went out of range"
error in the logs when this occurs).
- Solution: Check the logs to see which DNS
servers are failing or timing out and remove them. User fewer DNS
servers for best performance and ensure that you use reliable DNS
servers.
- Tip: If mail appears to be "sticking" in the
outbox check the sending log, it will show the failures, and
indicate which mail sent and which mail failed. If some mail is
being sent, then mail that is not being sent is failing for a
reason, and Email Server return the mail to the sender for permanent
failures and retry for temporary failures for up to 48 hours before
returning the mail to sender.
- Tip: If no mail is being sent at all check your
sending settings. If you are sending mail via MX sending ensure that
have specified a relay for sending via when MX sending fails. If you
are sending via a relay server then check that your authentication
details are correct.
C13) After upgrading to Email Server 4.2.0 the email seems slow and unresponsive (and
may be using an excessive amount of CPU time or memory)
Email server slowdowns and non responsive interface as a result of
the log files not being migrated correctly, causing the old XML entries
to be imported repeatedly. If this occurs it can be resolved as follows:
- Close Email Server and delete the All .TPS files from the
Email Server Data directory, except
DSSW4.TPS.
Under Windows XP, Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 this is:
C:\Document and Settings\All Users\Application
Data\Capesoft\Email Server\
Under Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 this is:
C:\ProgramData\Capesoft\Email Server\
Please do not delete DSSW4.TPS, or you
will have to re-register Email Server.
- Open the Logs sub directory in the
Data directory and delete all files that
it contains.
- Restart Email Server.
This will resolve the problem, which should not reoccur with the new
release.
C14)
After upgrading to Email Server it fails to start and displays an "unable to
reload license" error.
The license file is corrupt. Please delete the DSSW4.TPS file from the Data
directory:
Under Windows XP, Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 this is:
C:\Document and Settings\All Users\Application
Data\Capesoft\Email Server\
Under Vista, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 this is:
C:\ProgramData\Capesoft\Email Server\
You will then need to restart and re-register Email Server. If you do
not have a current activation code please email Capesoft Support and a new
activation code will be provided.
Sending Errors
F1. 553 SMTP Relay Denied
This error is caused for one of two reasons:
- You are attempting to send email to a domain that is not recognized by
this server
- You are attempting to relay email through this server, and have not
authenticated
Most likely you are seeing this message because you have not
authenticated. To use this server as a relay (to send email to an outside
address using your domain name), you must authenticate first.
You can do this in one of two ways:
- SMTP Authentication -
SMTP AUTH is a method for
verifying a user's login and password before allowing Mail to be sent to
other Mail Servers on the Internet. Email Server is required to login before
sending mail. This method allows you to simply enter your Username and
Password (the same ones you use for POP or IMAP) in the Send settings.
- POP before Send - This method allows Email Server to authenticate
by logging into a POP mail account. Once authenticated you are allowed to
relay for the next 15 minutes from your current IP address without further
authentication.
Glossary
Domain:
A Domain is just a fancy name for the last part of an email address. For
example:
microsoft.com is the domain for the email address
bill@microsoft.com.
ISP:
Internet Service Provider. It's the company that you get your Internet
Connection from. This may either be a dial-up service or a permanent
connection. If you don't know who this is try asking your network
administrator.
There are a lot of ISPs, they are companies like AOL, Juno, ComCast,
IAfrica, MWeb etc.











